Is Cast Iron Magnetic? – Know the Every Unknown
Cast iron lies among the popular and versatile materials. You can find its usage in almost every field of life. The common concern among many users regarding this material is “Is cast iron magnetic?”. The answer to this question is not so simple but depends on multiple factors including composition and type, etc. Uncover every single fact on the cast iron types, applications, and magnetic concepts. Sounds exciting? Let’s get started!
Insights on the Cast Iron Concept and Facts
You can define cast iron as a group of alloys featuring iron-carbon content. In these alloys the carbon content is greater than 2 percent. Higher carbon content within cast iron induces the properties like brittleness and high hardness. You can cast the cast-iron in any complex shape you want which is often difficult to accomplish with other metals. This castability property makes cast iron popular in the construction as well as automotive industries.
Key Cast Iron Types and their Magnetism
| Sr. No. |
Cast Iron Type |
Carbon Structure |
Magnetic Properties |
Magnetic Field Strength |
| 1 |
Gray Iron |
Graphite flakes |
Strongly magnetic |
High |
| 2 |
White Iron |
Carbide network |
Weakly magnetic |
Low |
| 3 |
Ductile Iron |
Nodular graphite |
Strongly magnetic |
Comparatively High |
| 4 |
Malleable Iron |
Temper carbon |
Strongly magnetic |
High |

Gray Cast Iron
The gray cast iron as the name implies feature gray appearance. This gray appearance is because of the existence of graphite flakes which resembles the flake like structure. It greatly influences the mechanical properties. The key properties of the gray cast iron includes:
- It has higher compressive strength which reflects this cast iron can bear heavy loads without contributing to deformation.
- The existence of graphite flakes in strcuture of this cast iron leads you to face easy machineability. You can easily drill, shape or cut your gray cast iron.
- You can use gray cast iron where you need to reduce vibration or noise. Gray cast iron can effectively damp up noise or vibration because of flakes’ strcuture
- It features brittleness and have lower tensile strength. You cannot use it in areas where you need high toughness and flexibility.
The key areas where you can us egray cast iron includes cookware, engine blocks, pipes, tool frames, etc. Higher machineability of this type of cast iron make it desireable among complex finishing and machining applications.
White Cast Iron
The white cast iron refers to a cast iron type which does not include graphite but include carbon. This gives the cast iron crystal white appearance when fractured. Some of the key properties that you need to know about the white cast iron includes:
- Existence of iron carbide makes white cast iron harder. It resist wear as well as abrasion strongly.
- The hardness induction because of iron carbide also makes this cast iron brittle. It features negligible ductility. You cannot bend it or stretch this type of cast iron.
- The white cast iron features excellent wear resistance. These attributes make it best for crushing and grinding applications.
- The white cast iron features lower machineability. You need special tools and processes to machine the white cast iron.
The key areas where you can use this cast iron are cement mixer lining, mill rolls, and crushers. You can also use it as wear resistance tool surfaces in heavy industry or mining.
Ductile Cast Iron
Another name of this cast iron is nodular cast iron. In this cast iron type the strcuture possesses round nodules rather than the flakes. Such microstructure transforms the mechanical properties hence enbedding higher toughness as well as ductility. The properties of the ductile cast iron are:
- You can easily use ductile cast iron where you need to subject the material to stretching forces. Higher tensile strength play a key role in this regard.
- When a force applied this cast iron can deform without resulting in fracture. This is mainly because of excellent ductility.
- It has higher strength and can absorb impact or loads without leading to fracturing. The ductile cast iron is ideal for structural applications.
- You can use it in automotive suspension as it can bear the load in repeated cycles. This is because of the superior fatigue resistance.
You can use ductile iron in automotive industry to make axles, crankshafts and various suspension components. You can also use ductile cast iron in formation of pressure vessels, pipelines, and other machinery types. It is ideal for applications which require toughness, strength, and ductility.
Malleable Cast Iron
When you heat the white cast iron to a temperature range of 900
0C to 950
0C for a specified duration. Then the resulting product will be malleable cast iron. In this process the cementite experience a transformation into irriegular shape graphite nodules. The properties of the malleable cast iron are:
- The malleable cast iron features excellent tensile strength. This makes this type of cast iron bear oulling forces without breakage or fracture.
- The ductility of the malleable cast iron is much more than what you get with the white cast iron. You can bent hammer, or twist this cast iron type.
- You can subject this malleable cast iron to sudfden forces application without any worries of breakage.
- The machineability of malleable cast iron is less than gray cast iron but still you can machine it to form the detailed parts.
You can use this cast iron type in manufacturing of brackets, pipes, or hand tools. Option exist to use the malleable cast iron in making suspension parts or steering knuckles, which require high ductility or toughness.
Compacted Graphite Iron
You can define this cast iron featuring a microstructure that lies in between that of ductile iron or gray iron. In compacted graphite iron, it features worm shape structure besides the nodules or flakes. It also offers combination of properties that you get with the ductile or gray cast iron such as:
- You can use it in structures which require more integrity because of higher tensile strength
- Because of higher thermal conductivity you can use it in higher heat dissipation applications
- It offers better castability than what you expect with the ductile iron
- The CGI can bear higher stress nad it also features higher mechanical or wear resistance
- It offers higher vibration as well as noise damping properties, hence making it suitable for industrial or automotive applications
Youcan use this type of cast iron in exhast manifolds, cylinder blocks or heads. This is because of the castability, higher strength, and thermal conductivity properties. You can also use it in industrial machinery which require both wear resistance and strength.
Physical Properties of Cast Iron Types
| Sr. No. |
Property |
Gray Iron |
White Iron |
Ductile Iron |
Malleable Iron |
| 1 |
Color |
Grayish-black |
White |
Grayish-black |
Grayish-black |
| 2 |
Hardness |
Medium |
Very hard |
Medium-high |
Medium |
| 3 |
Strength |
Moderate |
High |
comparatively High |
High |
| 4 |
Ductility |
Low |
Low |
Good |
Good |
| 5 |
Machinability |
Excellent |
Poor |
Comparatively Good |
Good |
| 6 |
Wear Resistance |
Good |
Excellent |
Good |
Good |
| 7 |
Heat Resistance |
Good |
comparatively Good |
Good |
Good |
| 8 |
Corrosion Resistance |
Good |
Fair |
comparatively Good |
Good |
| 9 |
Magnetic Properties |
Strongly magnetic |
Weakly magnetic |
Strongly magnetic |
Strongly magnetic |
| 10 |
Density |
7.1 g/cm³ |
7.3 g/cm³ |
7.2 g/cm³ |
7.2 g/cm³ |
| 11 |
Melting Point |
1150-1300 °C |
1200-1400 °C |
1150-1300 °C |
1150-1300 °C |
Is Cast Iron Magnetic?
Many concerns about “is cast iron magnetic”. Yes, the cast iron is magnetic. The main thing which play greater role in this regard is the iron content. It features a larger number of valence electrons in the outer shells. When you put the iron in the magnetic field the electrons align their movement in a way that contribute to magnetism. Electrons within the orbit not only spins but also revolves. As per the fact the chharges that feature opposite charge attract, the electrons spin in chnaged direction to that of the subjected field.
Will a Magnet Stick to Cast Iron?
Yes, The main thing which play the role in this regard is the higher Fe volume. As mentioned above the Fe carries the magnetic characteristics. The presence of free electrons in the valence shell makes the cast iron ferromagnetic substance. These materials show stronger attraction to the magnets.
Is Ductile Iron Magnetic?
Yes, the ductile iron is magnetic. Discovered in 1943 the ductile iron features higher graphite content. This is what contributes to the better magnetism properties. The spherical shape of the particles makes them ductile. Apart the spherical shape in this cast iron contributes to the zero defects or cracks. The hardness of this cast iron is lower but ductility is higher. You can define it as the ability to show greater attraction.
Is Cast Iron Pot Magnetic?
Yes, without any doubt. The higher amount of iron is responsible for this behaviour. You can experience the use of cast iron in induction cookware applications. The induction mainly results when the magnetic field heats the material. This only works with the utensils featuring higher magnetism. You can say that this cookware is perfect choice. Apart, you can use these cast iron pots on gas powered stoves.
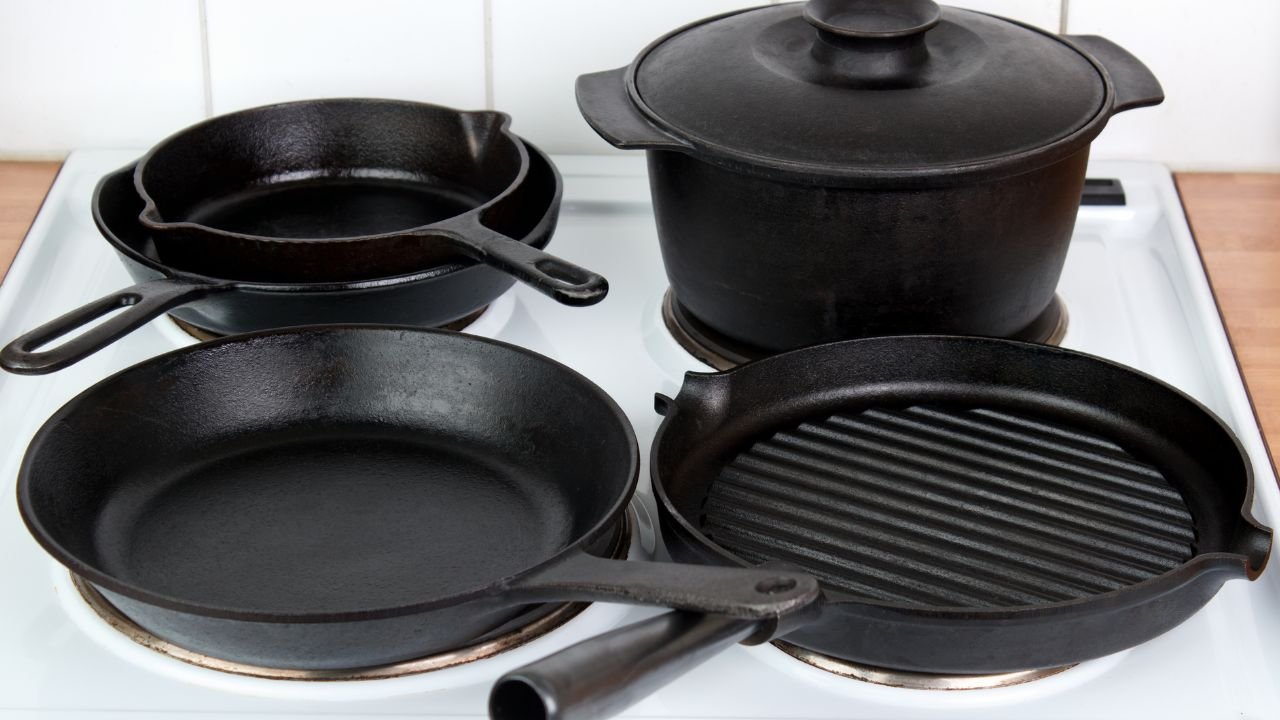

What is Cast Iron Used For?
You can utilize the cast iron in many applications such as:

- Cookware
- Cylinder Head
- Cylinder block
- Exhaust manifolds
- Pipes
- Pressure valves
- Structural applications
- Ball mills
- Cement mills
- Extrusion nozzles
- Drawing dies
The mentioned above are the few applications where you can utilize cast iron. This is mainly because of the properties like hardness, toughness, ductility, fatigue resistance, etc.
Conclusion
So summing up is cast iron magnetic? Yes the cast iron is truly magnetic. This is what contributes to the magnetic properties of the iron. Although the magnetic properties varies depending on the cast iron type including ductile cast iron, malleable cast iron, white cast iron etc. So many types and each with different characteristics contribute to the toughness, heat resistance, strength, etc. Getting insights on the cast iron magnetism can lead you to select right type for the right application. This will ultimately help you harness optimum functionality, performance, and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Iron Oxide Magnetic?
Yes, the iron oxide is magnetic in nature. Another name of iron oxide is magnetite. It refers to a naturally occuring oxide of iron. Because if iron content it exhibits magnetic properties.
Is Iron A Magnet?
Actually iron is magnetic but not a magnet itself naturally. Although you can magnetize iron.
Is Wrought Iron Magnetic?
Yes, wrought iton is magnetic. The main reason behind the wrough iron magnetism is the existence of iron content. Becuasse of this the wrought iron exhibits magnetic properties.
Is Iron Pyrite Magnetic?
No, Although it contains the sufficient iron content. The crystal structure and the complex composition prevent iron pyrite from showing the magnetic properties.
Is Iron The Only Magnetic Metal?
No, Other metals also exists which are magnetic. These metals includes nickel, cobalt are also magnetic. They exhibit magnetism because of the ferromagnetic nature.
Why Is Iron Magnetic And Wood Not?
The presence of valence electrons in the shells of the iron makes it magnetic. These electrons are responsible to contribute to the net magnetic moment which ultimately leads to attraction. Wood on the other hand does not possess any valence electrons. Hence you cannot experience any magnetic domain with wood. This is why wood is not a magnet.
Is Iron Filings Magnetic?
Yes, the iron fillings are magnetic. The term filling refers to the minute particles of metal iron. When you expose them to magnetic field these particles align themselves and shows attraction.
Is An Iron Nail Magnetic?
Yes iron nail is magnetic. The main reason behind its magnetism is the iron content. The iron a naturally occuring metal. It has free electrons in the valence sheel which ultimately becomes the reason for this magnetism. You can also magnetise the iron nails.
Read more:
Is Magnesium Magnetic? – Facts / Properties / Applications
Is Titanium Magnetic? – Properties/Applications/Analysis
Is Zinc Magnetic
Is Brass Magnetic?
is lead magnetic? Unveiling Properties, Implications, and Applications








One Response