Mastering Electroplating; An In Depth Guide

Table of Contents
ToggleElectroplating is essential, in industries as it enhances metal surfaces to resist corrosion and look attractive. This article explores the world of electroplating discussing its benefits, applications, methods and key considerations for implementation.
Exploring Electroplating
Electroplating is an used technique, in manufacturing that involves improving material surfaces by applying a layer of metal through a process.
It serves as a technique applied in sectors to improve material properties and aesthetics.
The electroplating process involves using a current to transfer metal ions from a solution onto the conductive workpieces surface creating either a protective or decorative layer. This process enables the application of metal coatings like gold, silver, copper, nickel, chromium and zinc.
How Electroplating Functions
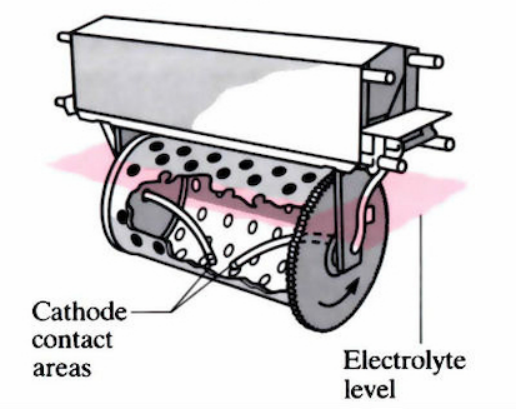
The electroplating procedure comprises four elements; the anode, cathode, plating solution and power source.
Anode
Usually composed of the deposited metal type for the workpiece; it experiences oxidation during electroplating to release metal ions into the solution.
Cathode
Serving, as the substrate or workpiece receiving the coating.
The charged electrode, known as the cathode plays a role in the electroplating process.
Plating Solution
In the plating solution, which is also referred to as the electrolyte there are dissolved metal ions of the chosen coating material.
Power Sourcing
To power this electroplating process a power source is utilized, in the form of a current (DC) power supply. This power source generates both voltage and current necessary for driving oxidation reduction reactions at both ends. Anode and cathode.
Electroplating Working Principle
The working principle behind electroplating is rooted in electrochemistry and electrolysis principles. When an electric current is introduced it attracts metal ions in electrolyte towards the charged cathode (workpiece). Here these ions undergo reduction. Get deposited on its surface gradually forming an even metal coat.
The electroplating process involves steps;
- Immersing the workpiece (cathode) into a solution containing metal ions, for deposition.
- Submerging an anode made of metal as desired coating into this solution.
- When an electric current is passed between the anode and cathode the metal ions, in the solution move towards the cathode.
- The metal ions are then. Deposited onto the surface of the workpiece at the cathode to create the desired metal coating.
- At that moment oxidation happens at the anode, which releases metal ions into the solution to ensure the balance.
Safety Precautions for Electroplating
When conducting electroplating processes it’s essential to prioritize safety for the well being of individuals and the environment. Here are some key precautions to consider;
- Maintain equipment regularly; Keep equipment in condition to prevent accidents and ensure proper functioning.
- Manage waste properly; Adhere to waste disposal regulations when getting rid of chemicals and byproducts generated during electroplating processes.
- Remember to wear Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), like gloves, eye protection and aprons to protect yourself from exposure to chemicals and metals.
- Stay ready for emergencies by setting up protocols for emergency responses such as eyewash stations, showers, evacuation plans and providing training on how to handle emergencies.
- Make sure all staff members involved in electroplating activities undergo training and certification.
- Handle chemicals cautiously by following guidelines, for storing mixing and disposing of electroplating chemicals to reduce the risk of accidents.
Different Electroplating Methods
Different industries employ a variety of methods each tailored to substrates and purposes. These methods encompass techniques designed for applications. Here are some used electroplating techniques;
Racking Plating;
In racking plating objects are hung from racks or frames to ensure a coating, across all surfaces. This method is suitable for items with shapes that require handling. It enables control over coating thickness. Allows for plating in specific areas.
Barrel Plating;
Barrel plating involves placing items such as screws, fasteners and components into a rotating barrel filled with the plating solution. The tumbling motion of the barrel ensures a coating on each piece making it an efficient and cost effective method for production of goods. Typically bulky or small items that do not need individual handling barrel plating.
Brush Plating;
In brush plating a portable brush or applicator is used to apply the plating solution to areas. Also known as spot plating or selective plating this method is ideal, for touch ups, spot repairs and coating sections of components. Brush plating offers flexibility and precision required for coatings without the complexity of setups or immersion tanks.
Continuous Plating;
Continuous plating, also known as strip plating or reel to reel plating is utilized to coat strips or reels of metal substrates. This method is commonly employed in the production of lead frames, terminals, connectors and various electronic components. Continuous plating is preferred for large scale manufacturing due, to its ability to provide coating thickness and efficient processing.
Steps for Panel Plating;
Panel plating involves coating sheet substrates such as metal panels and printed circuit boards (PCBs). Specialized equipment is used to ensure that metal coatings are evenly applied across the substrates surface. In applications requiring thickness control and uniformity panel plating plays a crucial role.
Jet Plating Technique;
Jet plating entails directing a stream of plating solution onto the substrates surface using a nozzle or jet. Also known as high velocity plating this method is particularly effective for applying coatings to areas that traditional techniques struggle to reach. Jet plating provides control over the plating process making it suitable for precision engineering and tooling applications.
Innovative Electroplating Approach;
Pulse plating is a modified form of electroplating where the electrical current is adjusted in bursts to achieve properties, in the plated material.
This method gives management over how metal ionsre spread, stick and form the structure of the deposited material. Pulse plating is often used in scenarios where fine structures and surface finishes are needed to improve the quality and effectiveness of coatings.
The choice of a method relies on factors, like the shape of the base material, production size, coating needs and cost aspects. Each electroplating technique provides benefits to cater to needs. By grasping the features and capacities of these methods manufacturers can select the one to fulfill their specific needs and attain the desired coating outcomes.
Suitable Metal Materials, for Electroplating
Metals, like nickel, chromium, copper, gold and silver can be applied onto surfaces using electroplating. The selection of metal depends on factors such as the intended use, base material composition and desired finish characteristics. Each metal brings its properties and applications to the electroplating process. Utilized metals in electroplating include;
- Copper; Recognized for its conductivity, conductivity and corrosion resistance.
- Nickel; Appreciated for its hardness wear resistance and ability to protect against corrosion.
- Chromium; Produces a lasting layer that provides resistance to wear and corrosion.
- Gold; Enhances aesthetics while offering conductivity and protection from corrosion.
- Silver; Highly regarded for its conductivity, thermal conductivity and appealing appearance.
- Zinc; Effective in protecting steel and iron substrates from corrosion.
- Tin; Deposits a coating with capabilities and resistance, to corrosion.
Pros and Cons of Electroplating
Advantages of Electroplating;
Electroplating is an used method, for surface finishing in industries due to its numerous benefits. Here are some key advantages of electroplating;
- Enhanced Protection Against Corrosion;
The coatings applied through electroplating serve as a barrier against moisture, chemicals and environmental factors effectively shielding metal substrates from corrosion. This helps prolong the lifespan of components exposed to conditions such as equipment, outdoor fixtures and automotive parts.
- Increased Durability Against Wear;
By enhancing hardness and resistance to wear electroplated coatings minimize surface wear, friction and damage caused by abrasion or contact with materials. This makes components for applications where mechanical stresss common like cutting tools, bearings and machine parts.
- Improved Visual Appeal;
The use of metal coatings like brass, nickel, gold and chrome enhances the aesthetics of objects. Considering the importance of aesthetics in customer satisfaction electroplated items are becoming increasingly popular in sectors such as design, jewelry making, automotive industry and consumer goods.
- Uniform Coating Thickness;
The precise control offered by electroplating over coating thickness enables application on shapes and tight tolerances. This uniformity enhances both the performance and appearance of items in situations where consistent coating’s crucial, for functionality.
Customizing the surface properties, such, as conductivity, lubrication and adhesion through electroplating allows for creating tailored solutions to meet application needs. By selecting the plating materials and adjusting process parameters the functionality and effectiveness of plated components can be improved by attaining the desired surface characteristics.
The slight increase in material thickness during electroplating ensures that the dimensional precision of substrates remains intact making it well suited for precision engineering and manufacturing applications where maintaining dimensionss essential.
Versatility
Versatility is a feature of electroplating as it can accommodate substrates such as metals, plastics, ceramics and composites. This flexibility provides designers and manufacturers with an array of choices for material selection across industries and production requirements.
Electroplated coatings like gold and silver are recognized for their conductivity and solderability. They are commonly utilized in applications to ensure electrical connections, efficient signal transmission and effective component soldering for optimal performance.
Advancements in electroplating technology have resulted in eco alternatives such as cyanide solutions and trivalent chromium plating. These alternative methods aim to minimize the impact of electroplating processes by addressing concerns related to energy consumption, usage efficiency and waste management practices.
Cost Effective options
Electroplating offers cost options, for achieving desired performance levels and aesthetics at prices.
Electroplating plays a role, in reducing waste and cutting costs in manufacturing by offering coating and surface finishing choices that optimize process parameters and material usage.
Drawbacks of Electroplating;
Electroplating processes can result in the generation of waste and byproducts that require proper disposal and treatment.
The electroplating process involves steps that necessitate precise control, over various parameters to maintain consistent quality standards.
In the field of electronics electroplating is a practice, for creating coatings preventing corrosion and enhancing solderability.
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) often feature electroplated copper traces for component attachment and electrical conductivity. Gold or silver plated connectors, contacts and terminals help improve conductivity reduce contact resistance and ensure connections in devices like computers, cellphones and consumer electronics.
Applications of Electroplating
When it comes to aerospace and defense applications that prioritize durability, performance and reliability electroplated parts play a role.
These coatings offer corrosion protection wear resistance and fatigue strength to aircraft components such as landing gear, hydraulic fittings and fasteners. Military equipment like guns, ammunition and optical instruments benefit from finishes that enhance functionality, durability and camouflage effectiveness in environments.
Electroplating’s widely utilized in the manufacturing of jewelry items,
home decor pieces
and decorative ornaments.
Items, like jewelry pieces
watches,
and upscale accessories receive finishes through gold,
silver,
and rhodium plating.
The beauty of hardware, lighting fixtures and decorative accents, in homes, hotels and commercial spaces is enhanced through the plating of brass, nickel and bronze.
In the field of instruments and devices electroplated coatings are utilized to ensure corrosion resistance, sterilization capabilities and biocompatibility.
These finishes are applied to tools, implants and diagnostic equipment to make them compatible with the body while also being resilient to sterilization processes in hospital settings.
When it comes to appliances and consumer goods electroplating is employed to improve performance, longevity and aesthetics. Chrome plated showerheads, handles and faucets in kitchens and bathrooms are not visually appealing but easy to maintain and resistant to corrosion.
Additionally electroplated finishes help prolong the lifespan of household appliances such as ovens, refrigerators and washing machines by safeguarding them against scuffs, abrasions and chemical exposure.
In machining and metalworking industries, coatings that enhance lubricity,dimensions stability and wear resistance play a role, in improving tooling efficiencyand machined components durability.
Electroplated coatings, like diamond, carbide and nickel are applied to cutting tools, molds, dies and precision components in industries such as metalworking, aerospace and automotive to improve cutting performance surface quality and tool durability.
In the realm of energy and environmental applications electroplating finds its place in technologies like fuel cells renewable energy systems and water treatment. The efficient electrochemical processes enabled by coatings on electrodes, membranes and catalytic surfaces play a role, in promoting sustainability through pollution removal and energy conversion.
The diverse applications of parts showcase their versatility and importance across industries. They contribute to advancements, product uniqueness and performance enhancement.
How to Pick the Suppliers, for the Electroplating Process
Choosing the suppliers is a critical factor in overseeing the electroplating process and ensuring both quality and cost effectiveness of the end product. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting suppliers for electroplating; Opting for notch electroplating providers entails taking into account essential factors to ensure top tier services at reasonable prices. Below are some aspects to bear in mind when picking suppliers;
Expertise and experience;
Seek out suppliers with a track record in the field possessing expertise in the specific metal coatings and techniques needed for your particular application.
Look for providers with experience, in electroplating; they will have an understanding of the process and be better equipped to handle intricate projects. Check if they have a history of meeting deadlines and delivering results.
Quality of materials;
Confirm that the suppliers can deliver quality raw materials, including anode metal, electrolyte solution and other consumables as these inputs directly influence the final product.
The caliber of materials utilized in electroplating can significantly affect the end outcome. Ensure that your providers use top notch products that meet your specifications and originate from sources.
Check the delivery promises of your suppliers. Can they meet your deadlines? Do they have a setup, in place to ensure timely delivery?
Assess the production capabilities of the supplier including their production capacity, equipment and quality control processes to confirm they can fulfill your quantity and quality needs. Consider their ability to handle projects or high volumes. Do they have the tools and technology to maintain efficiency and quality standards?
Confirm if your suppliers have certifications like AS 9100 & ISO 9001;2015 indicating their commitment to quality control measures and industry norms. Ensure that the supplier follows industry standards, environmental guidelines and safety protocols for risk management and compliance.
Select a vendor who’s responsive to your requirements offers communication and is open to resolving any issues collaboratively. Opt for suppliers who’re transparent about their operations, expenses and delivery timelines. Make sure they have a communication strategy, in place to keep you updated throughout each project phase.
Consider the equipment and technology utilized by your suppliers.
Are they, up to date on the advancements in electroplating? Do they have the equipment to handle projects?
Pricing Comparison;
Check out suppliers pricing and fee structures to make sure you’re getting the bang for your buck.
Reputation and Customer Relations;
Learn more about your suppliers track record by reading reviews reaching out to references or checking their ratings. Ensure they are responsive to your needs and have a history of delivering top notch customer service.
Ensure you get the deal by comparing prices from providers. Be cautious of prices as they could indicate lack of experience or subpar quality.
Proximity Considerations;
Take into account the suppliers location and transportation logistics as this can impact costs and turnaround times.
Confirm that your suppliers adhere to safety and environmental standards. The reliability and longevity of your electroplating process rely on this.
By assessing and choosing suppliers you can guarantee the quality, cost effectiveness and timely delivery of your electroplated components ultimately improving the overall efficiency and competitiveness of your manufacturing operations.
In Search of a Seasoned Partner for your Electroplating Requirements?
Look to Masion Company for notch electroplating services. They have a reputation, for excellence and expertise in the field making them the ideal choice for your electroplating needs.
Masion Company prides itself on having a team of professionals who excel in electroplating ensuring that each project meets high quality standards with precision. Their state of the art facilities are equipped with technology to provide results tailored to your specific requirements.
The company is committed to maintaining quality control measures guaranteeing flawless finishes and lasting coatings.
Understanding that every client is unique, Masion Company offers customized solutions for needs such as coatings, corrosion protection and specialized finishes. They also prioritize sustainability by adhering to eco practices and responsible waste management guidelines.
By partnering with Masion Company you can expect an effective process from start to finish. Benefit from their industry leading expertise that surpasses expectations and delivers outcomes. Get in touch, with Masion Company today to explore how their electroplating services can enhance the quality and performance of your products. Consider Masion Company as your partner, for all your electroplating needs.
In Summary
Electroplating is an widely embraced technique for surface finishing that significantly enhances the properties and performance of materials and products.
Understanding the basics, methods and optimal strategies of electroplating allows manufacturers to leverage this technology to improve the strength, aesthetics and performance of their goods.
This ultimately fosters innovation and competitiveness within their industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the primary components of an electroplating system?
The key components of an electroplating system consist of the cathode, solution and power source.
- Which metals are commonly used in electroplating?
Metals commonly employed in electroplating include copper, nickel, chromium, gold, silver, zinc, tin and others based on desired surface properties and applications.
- What are the advantages of electroplating?
There are benefits associated with electroplating such, as enhancing surface characteristics versatility, in application, cost efficiency, precise thickness management and complete coverage.
- What are the disadvantages of electroplating?
Regarding the drawbacks of electroplating potential issues include impact the complexity of the process limitations on materials the risk of defects and a high upfront cost.
- What are the common applications of electroplated parts?
Electroplated parts find applications in industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, machinery, jewelry making and oil and gas sectors to enhance surface characteristics and overall performance.
- How can customers choose the right suppliers for the electroplating process?
To select suppliers for electroplating services it is essential to consider factors such as,
expertise in the field quality of materials used in the process
manufacturing capabilities,
adherence to regulations,
level of customer support provided
pricing structure,
and proximity, to your location.

Send Your Inquiry Today


+86-18969433502
sales@sheetmetalmasion.com