Does Stainless Steel Rust – The Ultimate Guide
Stainless steel because of the key properties including considerable strength and corrosive resistivity features widespread usage in diverse industries. You can find the usage of stainless steel in kitchen cutlery, surgical equipments, construction tools, as well as jewelry to name a few. In this debate the question arises “Does stainless steel rust?” The main objective of this blog post is to throw light on stainless steel corrosion properties, causes, as well as prevention measures. Sounds exciting? Let’s dive right in!
Table of Contents
Toggle
Understanding Stainless Steel Composition
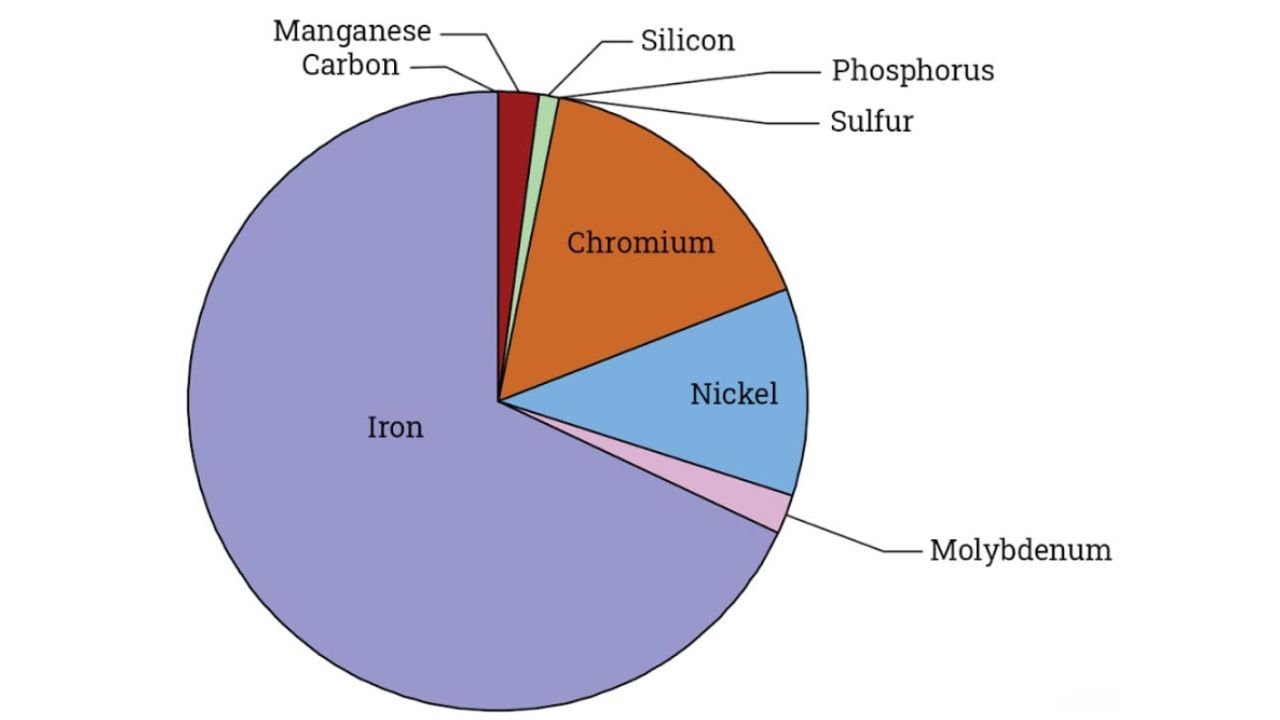
The total elements that plays a key role in the composition of the stainless steel are around 10. Each have a specific percentage ranging from 0 to 100 percent. You can get deeper insights by viewing through the table below:
| Sr. No. | Element | Purpose | Typical Range |
| 1 | Iron (Fe) | Base metal | 70 – 80% |
| 2 | Chromium (Cr) | Provides corrosion resistance | 10.5 – 26% |
| 3 | Nickel (Ni) | Improves ductility, toughness, and corrosion resistance | 0 – 25% |
| 4 | Molybdenum (Mo) | Enhances resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion | 0 – 3% |
| 5 | Manganese (Mn) | Improves strength and workability | 0 – 2% |
| 6 | Silicon (Si) | Deoxidizer, improves strength | 0 – 1% |
| 7 | Carbon (C) | Affects strength and hardness | 0.03 – 1.2% |
| 8 | Nitrogen (N) | Improves strength and corrosion resistance | 0 – 0.25% |
| 9 | Phosphorus (P) | Improves machinability | 0.01 – 0.04% |
| 10 | Sulfur (S) | Improves machinability | 0.01 – 0.03% |
As mentioned above each element plays a key role in imparting specific characteristics within the stainless steel. For instance the iron with maximum percentage within the stainless steel act as a base metal. While chromium is the element with second high percentage and this element is what imparts the corrosion resistance features to stainless steel. You can refer to the above table for the other elements role in the stainless steel.
Does Stainless Steel Rust? Factors Affecting Corrosion
Yes, it is true that the stainless steel can rust. But this is only true in some certain conditions. The main reason is that multiple factors play their part in this regard. Some of the key factors include:
Chlorine Exposure
In case if your stainless steel product or equipment comes in contact with the chlorine salt then it can results in corrosion. The timeframe greatly influence the resultant corrosivity. If you keep the equipment greatly in contact with the salts then you can experience a great level of corrosion.
Moisture and Humidity
Subjecting the stainless steel to the high humid environment can contribute to rust. The main reason is water provides the favourable conditions which promotes corrosion.

Pollutants from Industry
The prolonged exposure to the nitrogen as well as compounds of sulfur can lead you to experience the stainless steel corrosivity.
Acidic Substances Interaction
Acids act as a harsh substances in contributing to the corrosion of the stainless steel. It breaks down the film of chromium oxide that present on the stainless steel. Hence making stainless steel vulnerable to corrosion. The key substances includes acidic chemicals, foods, or acidic cleaners, etc.
Mechanical Damage
Dents or scratches can negatively impact the chromium oxide layer. Presence of no chromium oxide layer can leads your stainless steel become rusty.
Revealing Insights on Main Stainless Steel Categories
All the grades of the stainless steel that exists today has divided into different classes such as:
Austenitic
The austenitic steel grades are popular because they feature a comparatively higher percent of chromium content. This is the fact why Austenitic steels reflects better corrosion resistance features. In general it is not magnetic but you can make it so.
Ferritic
The ferritic class of stainless steel is magnetic and is cheaper. The main thing which contributes to their lower cost is lower nickel content.
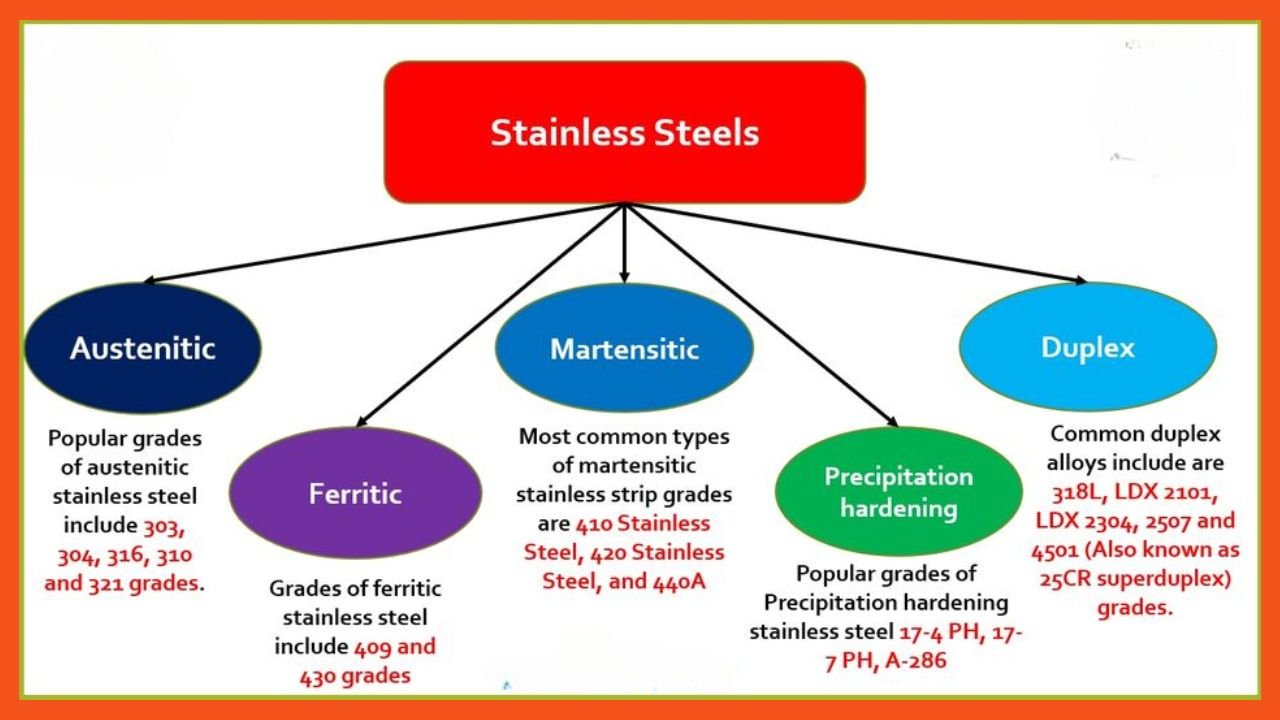
Martensitic
The less common in comparison to the other classes. Mainly because of the lower rust resistivity than what austenitic or ferritic offers. Regardless they have better strength features. The impact resistance as well as tensile strength of these steels is exceptional.
Duplex
The term duplex indicates that this steel comes from the combination of the austenitic as well as ferritic steels. You can expect incredible corrosion resistivity from these alloy grades. Option exist to incorporate these alloys in the gas industry or oil sector for piping systems establishments.
Precipitation Hardening
The PH class of stainless steels feature both durability as well as rust resistance. You cannot question the strength of these alloys. The common applications of these alloys includes gas, aerospace, nuclear as well as oil sector.
The following section will illuminate the highlights on the different grades of each class along with their resistivity and composition.
Different Stainless Steel Grades and Their Susceptibility to Rust
Let’s uncover the facts on each class:
Does 300 Series Stainless Steel Rust? – Austenitic Stainless Steels (300 Series)
Get insights on each grade composition and resistivity of the stainless steel that fall under this category.
| Sr. No. | Grade | Answer | Rust Resistance | Chromium (%) |
| 1 | Does 301 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Good | 16-18 |
| 2 | Does 302 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent | 17-19 |
| 3 | Does 303 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent | 17-19 |
| 4 | Does 304 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent | 18-20 |
| 5 | Does 316 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent (resistant to chloride pitting) | 16-18 |
| 6 | Does 304L Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent (low carbon content) | 18-20 |
| 7 | Does 305 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent | 17-19 |
| 8 | Does 308 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent | 19-21 |
| 9 | Does 316L Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent (resistant to chloride pitting, low carbon content) | 16-18 |
| 10 | Does 321 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent (resistant to carbide precipitation) | 17-19 |
Does 400 Series Stainless Steel Rust? – Ferritic/Martensitic Stainless Steels (400 Series)
Get insights on each grade composition and resistivity of the stainless steel that fall under this category.
| Sr. No. | Grade | Answer | Rust Resistance | Chromium (%) |
| 1 | Does 409 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Good (prone to pitting in severe environments) | 11-13 |
| 2 | Does 410 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Good (more resistant to pitting than 409) | 12-14 |
| 3 | Does 416 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Good (contains sulfur for machinability) | 13-15 |
| 4 | Does 420 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Good (hardening grade) | 12-14 |
| 5 | Does 430 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent (high chromium content) | 14-18 |
| 6 | Does 440A Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent (hardening grade) | 16-18 |
| 7 | Does 440B Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent (hardening grade) | 13-15 |
| 8 | Does 440C Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent (hardening grade) | 17-19 |
| 9 | Does 443 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent (resistant to chloride pitting) | 16-18 |
Does Precipitation Hardening Series Stainless Steel Rust?
Get insights on each grade composition and resistivity of the stainless steel that fall under this category.
| Sr. No. | Grade | Answer | Rust Resistance | Chromium (%) |
| 1 | Does 17-4 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent | 16-18 |
| 2 | Does 18 0 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent | 18 |
| 3 | Does 18 10 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent | 18 |
| 4 | Does 18 8 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent | 18 |
| 5 | Does 18 Gauge Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent | 18 |
| 6 | Does 18-8 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent | 18 |
| 7 | Does 18/0 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | Excellent | 18 |
Does Duplex (Ferritic-Austenitic) Series Stainless Steel Rust?
Get insights on each grade composition and resistivity of the stainless steel that fall under this category.
| Sr. No. | Grade | Answer | Chromium (%) | Rust Resistance |
| 1 | Does 201 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | 16-18 | Good (prone to pitting in severe environments) |
| 2 |
Does 202 Grade Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | 17-19 | Excellent (more resistant to pitting than 201) |
| 3 |
Does 2205 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | 21-23 | Excellent (high chromium content, good resistance to chloride pitting) |
| 4 | Does 2304 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | 18-20 | Excellent (similar to 304) |
| 5 | Does 2507 Stainless Steel Rust? | Usually No, Depends on Conditions | 25-27 | Excellent (very high chromium content, excellent resistance to chloride pitting) |
Types of Corrosion in Stainless Steel
Various types of corrosion exist in the stainless steel. Some of the key corrosion types that you can witness are:

- When you observe the small rusting spots on your stainless steel then it is pitting. These may develop up because of the localized damages.
- In crevices when they experience the moisture incorporation, then the moisture build up favourable conditions that leads you to experience the rust build up,
- If a certain point on the tool or equipment receive stress for long periods then it may develop cracks. These cracks because of harsh environment may face rusting.
- In the last you can experience the galvanic corrosion. This becomes prominent when dissimilar metals incorporate with each other or interact.
Common Substances and Their Effect on Stainless Steel Rusting
Get insights on how different substances influence the rusting of stainless steel:
Does Alcohol Rust Stainless Steel?
Alcohol does not promote or contribute to the rusting phenomenon of the stainless steel. But if you put the stainless steel in strong alcohol for comparatively longer time then it may leads to corrosion.
Does Citric Acid Remove Rust from Stainless Steel?
Yes, you can remove the layer of the rust from the stainless steel using the citric acid. It does not cause any kind of damage to the metal underlying.
Does CLR Clean Rust Off Stainless Steel Flat Grill?
Yes, this substance specially designed to remove rust as well as mineral deposits. Using this chemical you can efficiently clean rust from flat sheets or grills.
Does Coke Remove Rust from Stainless Steel?
The coke mainly comprises of phosphoric acid. It helps you get rid of rust. But please note after removing the rust you need to wash off the sugary residue left behind to prevent staining in future.
Does Baking Soda Remove Rust from Stainless Steel?
No because of the mild level abrasiveness it cannot remove the rust 100%. But using it you can scrubb away stains of the rust.
Does Bleach Cause Rust on Stainless Steel?
No, but you can make use of bleach to remove or disinfect the stainless steel surfaces.
Does Hard Water Cause Rust on Stainless Steel?
Yes, no doubt hard water contribute to the development of rust on your stainless steel. This is true specifically for the high mineral content.
Does Hydrogen Peroxide Rust Stainless Steel?
No, it does not lead you to face corrosion or rust on the stainless steel. Rather it aids you in removing the rust.
Does Lemon Juice Rust Stainless Steel?
Yes, because of the presence of the citric acid which can cause pitting, while the lemon juice can assist in removal of the stainless steel rust.
Does Vinegar Cause Rust on Stainless Steel?
Yes somehow it causes itching if you make it subject to long term exposure to vinegar. The vinegar is actually an acetic acid. It also help you remove the rust from stainless steel.
Stainless Steel Products and Their Susceptibility to Rust
Get insights on the different stainless steel products and what conditions may leads them to rusting in the table below:
| Sr. No. | Product | Rust Susceptibility |
| 1 | Does a Stainless Steel Exhaust Rust? | Generally resistant, but prolonged exposure to extreme conditions (e.g., salt, high temperatures) can lead to pitting or corrosion. |
| 2 | Does a Stainless Steel Sink Rust? | Generally resistant, but improper cleaning or exposure to harsh chemicals can cause staining or surface damage. |
| 3 | Does Stainless Steel Jewelry Rust? | Generally resistant, but prolonged contact with sweat, chlorine, or other corrosive substances can accelerate wear and tear. |
| 4 | Does Surgical Stainless Steel Rust? | Highly resistant to rust and corrosion, making it ideal for medical applications. |
| 5 | Does Titanium Stainless Steel Rust? | Not a type of stainless steel. Titanium is a separate metal with excellent corrosion resistance. |
| 6 | Does Stainless Steel Need Final Protective Finish to Avoid Rusting? | While many stainless steel grades are naturally resistant to rust, a protective finish (e.g., passivation, coating) can enhance its durability and appearance, especially in harsh environments. |
Why Does Stainless Steel Rust in Certain Situations?
Why Does Bathroom Stainless Steel Rust?
About bathroom stainless steel, it will rust for many reasons such as condensation or damp in the bathroom, including contact with water or cleaning reagents that contain chlorine or acid, which reduces the stability of the chromium oxide layer.
Why Does My Stainless Steel Knives Rust and Pit?
Stainless steel knives corrode and develop pits when washed with water or come in contact with acidic foods or detergents when not dried as soon as possible or when left in a wet place.
Why Does My Stainless Steel Pot Have Rust?
Stainless steel pots rust over long periods of time in contact with water, salts or acidic food residues that compromise the chromium layer thus leading to rusting.
Why Does Solid Stainless Steel Rust on a BBQ?
Barbeque accessories made from stainless steel rust due to the effects of high heat, greasy build-up and exposure to moisture if it is not washed frequently. Acid or salty marinades can also cause corrosion of the surface of the metal.
Why Does Stainless Steel Door Rust or Tarnish?
Weathering causes the stainless steel doors to either corrode, or lose their shiny finish through contact with moisture, salty air, or other chemicals. Any mark or abrasion on the protective cover will reduce the period before corrosion starts.
Why Does Stainless Steel Exhaust Rust?
Stainless steel exhausts are corroded by heat, road salts, and by moisture. With time, heat reduces the strength of steel.
Why Does Stainless Steel Flatware Rust?
Stainless steel utensils turn rusty when they are washed and left wet or come into contact with acidic foods and strong washing solutions used especially in dishwashers which ultimately reduces the outer cover of the utensils.
Preventing Rust on Stainless Steel
- Clean Regularly: Clean the stainless steel area because the presence of moisture and highly corrosive materials should be avoided.
- Choose the Right Grade: Employ better quality of stainless steel where conditions associated with high corruption are evident.
- Apply Protective Coatings: Coat the steel with specialized coatings to give them another layer to protect them from their surroundings.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Do not use bleach or other acids as they may wear off the outer chromium oxide layer.

Conclusion
It is right that the stainless steel effectively resist rust but you can prevent it may rust in specific circumstances. Moisture, salt, mechanical damages can affect the outer chromium oxide layer which is preserving the surface of the materials. The best approach to avoiding rust is to be aware of the various kinds of stainless steel and the manner in which they behave in particular settings. It is therefore of profound importance to clean and maintain your stainless steel products regularly and to ensure that you use the right grade for the right environment.
FAQs
How Fast Does Stainless Steel Rust?
The rate of rusting of the stainless steel depends on the surroundings. In seawater rust can develop relatively faster due to the action of salt while in a sealed and dry atmosphere, it might take ages before rust sets in.
Does Stainless Steel Rust in Water?
Stainless steel as a material is not inclined to rust when used in fresh water situations. Nevertheless, constant exposure of the surface to water without adequate protection would result in rusting, especially if the water is mineral or acidic.
Does Stainless Steel Rust in Salt Water?
Indeed, rust is much more likely to occur regarding the presence of salt water. The chloride ions of the saltwater tend to destroy the protective chromium oxide layer hence causing the rusting process.
Read more:




One Response