What is NEC Code for Junction Boxes?
Are you looking for a junction box to setup at your home or on office. You cannot ignore the importance that NEC code for junction boxes. Wondering what is NEC code, what guidelines you need to follow to ensure adherence? No worries, your search ends here. This article will provide in-depth insights in this regard.
Table of Contents
ToggleNEC Code for Junction Boxes Overview
The National Electrical Code refers to a standard build by United States to facilitate proper wiring of electrical systems. It is a set of guidelines covering safety precautions as well as electrical installation practices sought to eliminate risks for example fires or electric shocks. The NEC is legally required to be followed for all residential and commercial structures, as it details the correct methods to safely install electrical systems. The primary purposes of NEC are to safeguard life and property against electrical risks with a mission of securing safety to electrical work. It provides straightforward and comprehensive rules for how electrical systems ought to be installed, constructed and maintained in order to prevent risks.How the NEC is Updated and Maintained
The NEC is revised every three years to capture new technology, address new hazards, and reflect developments in the electrical world. It is reviewed and updated by a panel of experts to continuously reflect current practices in ensuring electrical safety.Understanding Junction Boxes
Definition of a Junction Box
The term Junction Box can also be defined as a synthetic container that consists of one component and can be fixed or moveable. Junction box can be defined as an enclosure that is intended to cover the connections whether they are in the form of splices or terminals. It is also useful as a point of convergence where two or more wires can be connected and managed, with minimal dangers of electrical fire.
Common Uses and Applications
Junction boxes are utilized in residential, commercial as well as Industrial electrical installations. These are crucial in joining the wires and shielding the electrical connections from various conditions that may arise while wiring installations are being conducted.Importance in Electrical Systems
The conceptual understanding of the importance of junction boxes in providing reliability and safety to electrical systems. They help avoid communication with live wires, shield connections from moisture and dusty environments, and ensure easier inspection and fixing of electrical connections.NEC Codes for Junction Boxes to Follow Before Installation
In the following section we will uncover insights on nec regulations governing pull and junction boxes:
NEC 314.28: Guideline for Junction Box Material
The first NEC code for junction boxes refer to material selection. Let’s uncover what it entails:Approved Materials for Junction Boxes
NEC 314.28, junction boxes shall be made of some material which will not burn such as metal or some type of plastic. The material used needs to correspond to the conditions of the location where the junction box will be placed; the availability of the material for damp/wet conditions should be considered.Construction Standards and Durability
Some essential considerations when designing junction boxes involve materials and their ability to withstand certain conditions such as UV light, corrosion, and moisture. Metals such as stainless steel and aluminum are some of the examples of materials that you need to consider because of low corrosion rates.Weatherproof and Non-Weatherproof Options
Weather resistant junction boxes and non-weather resistant junction boxes exist. Outdoor junction boxes must comply with the harsh external weather conditions. General purpose boxes are designed to be used exclusively indoors where they will not be exposed to direct moisture.NEC 314.16: Volume Size of the Junction Box
For 314.16 nec metal electrical junction box sizes follow these regulations:Calculating the Correct Size
NEC section 16 provides requirements for the electrical junction box dimensions in relation to the number and size of conductors accommodated in the boxes. It is expressed in cubic inches and provides enough volume to accommodate all wires and devices.Considerations for Wire Count and Size
The size and quantity of the conductors determine the volume of the junction box to be used. For instance, a box with three to six conductor needs at least 18 cubic inches of the volume and a box with seven to eight conductor needs at least 20 cubic inches of the volume.Box Fill Calculations and Allowances
The minimum distance between junction boxes should be carefully calculated to prevent overloading and problems with electric wiring. The NEC offers clear instructions for determining the volume or junction box depth depending on the conductor’s size, the device volume, and other fittings contained in the box.NEC 370-29: Junction Box for Hazard Locations
In some cases, junction boxes should be made from materials that can be used in specified hazardous areas. These boxes should not allow the escape of flammable gases or vapors and should incorporate grounding to eliminate the risk of static electricity. Other important markings include the hazardous location classification and the maximum temperature allowed.NEC 314.29: Junction Boxes for Non-Hazard Locations
Junction boxes for non-hazard areas, you need to locate where they can be easily accessed for inspection and maintenance. They should be firmly secured to eliminate movements and vibrations that could lead to loosening; their covers should be well tightened to minimize cases of touching live conductors.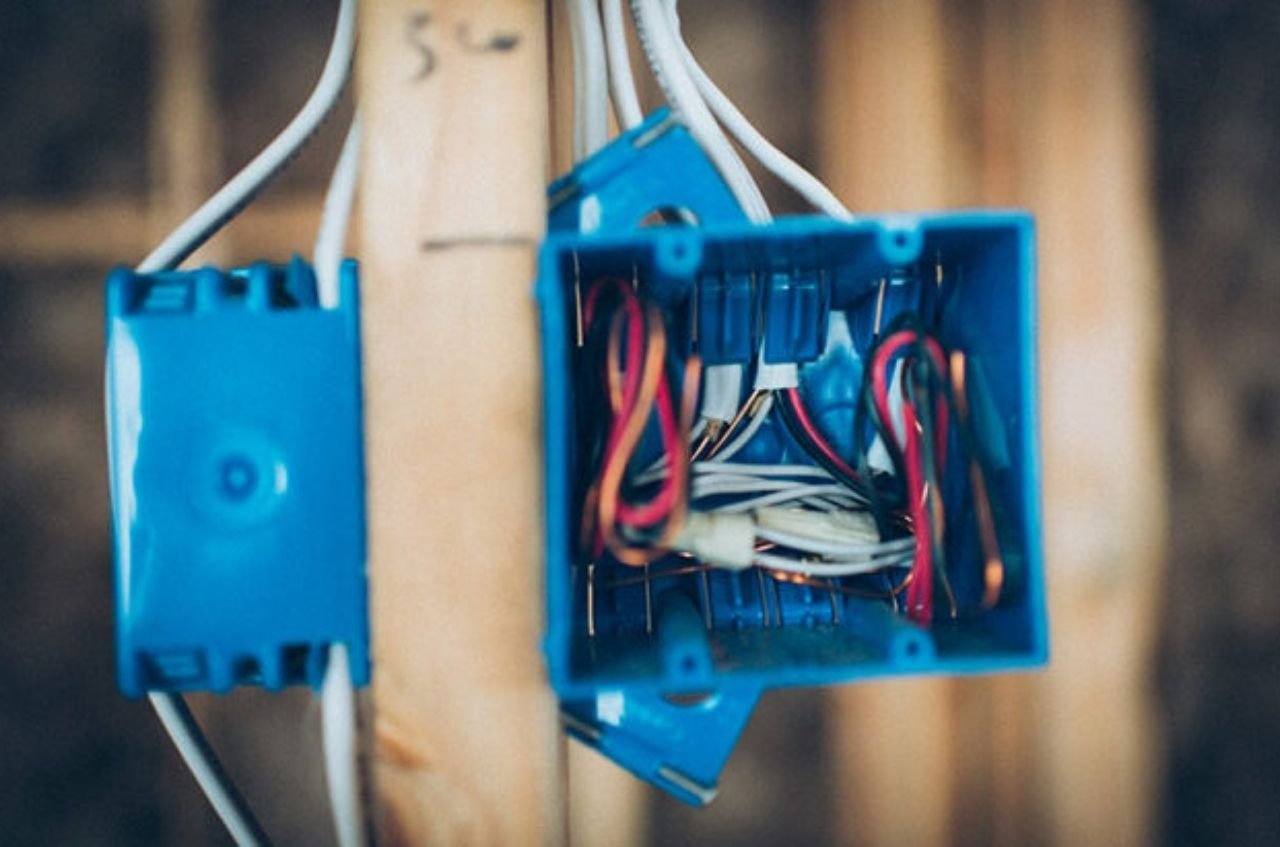
NEC 250.110: Guidelines for Junction Box Grounding
Grounding Requirements
NEC article 110 requires that junction boxes be grounded to ensure fault current has a path through which it can return to its source. This aids in eliminating electric shock hazard while enhancing overall security.Grounding Methods and Conductor Size
The grounding method should be suitable for the junction box material; for instance, metal boxes should have grounding screws, among other methods. The grounding conductor should be of a size compatible with the junction box and should be continuous and unbroken.Special Considerations for Non-Metallic Boxes
The non-metallic junction boxes also must be grounded. An approved grounding clip shall be used to connect the grounding conductor to the box and this shall be done by installing the clip in a factory made hole.NEC 110.26: Guidelines for Clearance
The article 110.26 nec involves following regulations:Clearance Area Requirements
NEC rule 110.26 deals with the required electrical box clearance and other electrical parts. The work space must have a minimum dimension of 36 inches depth and 30 inches width for operation and maintenance safety.Height and Headroom Clearance
The minimum headroom clearance is 6 feet with the working space height depending on the voltage of the equipment. This affords sufficient grounds for secure and inclusive environments for working conditions.Accessibility and Maintenance
The clearance area must be open to allow easy access and it must also be open for maintenance features. It should be possible for the junction box to allow the opening of equipment doors to a 90-degree angle to allow easy access and operation.Cover Requirements
NEC Standards for Junction Box Covers
NEC regulates the type of exterior junction box cover that should be used in junction boxes to ensure that they are properly fitted and offer desired level of protection. Hoods prevent direct touch with live wires and also shield the electrical connections within the box.Types of Covers
There are two main types of covers: solid and ventilated. Solid cover enclosures offer a contained environment while the ventilated covers allow for the flow of air, this is useful where there is a threat of over heating in some uses.Importance of Using Approved Covers
Therefore it is crucial to use NEC approved covers to ensure safety and compliance is observed. Correctly installed covers protect the junction box from dust, moisture, and other particles, which are necessary for secure performance.Conduit and Cable Entries
Guidelines for Conduit and Cable Entries
The NEC offers specific rules for conduit and cable entries into junction boxes. The connectors and fittings used should be of appropriate sizes that fit well to avoid damaging the conductors when making connections.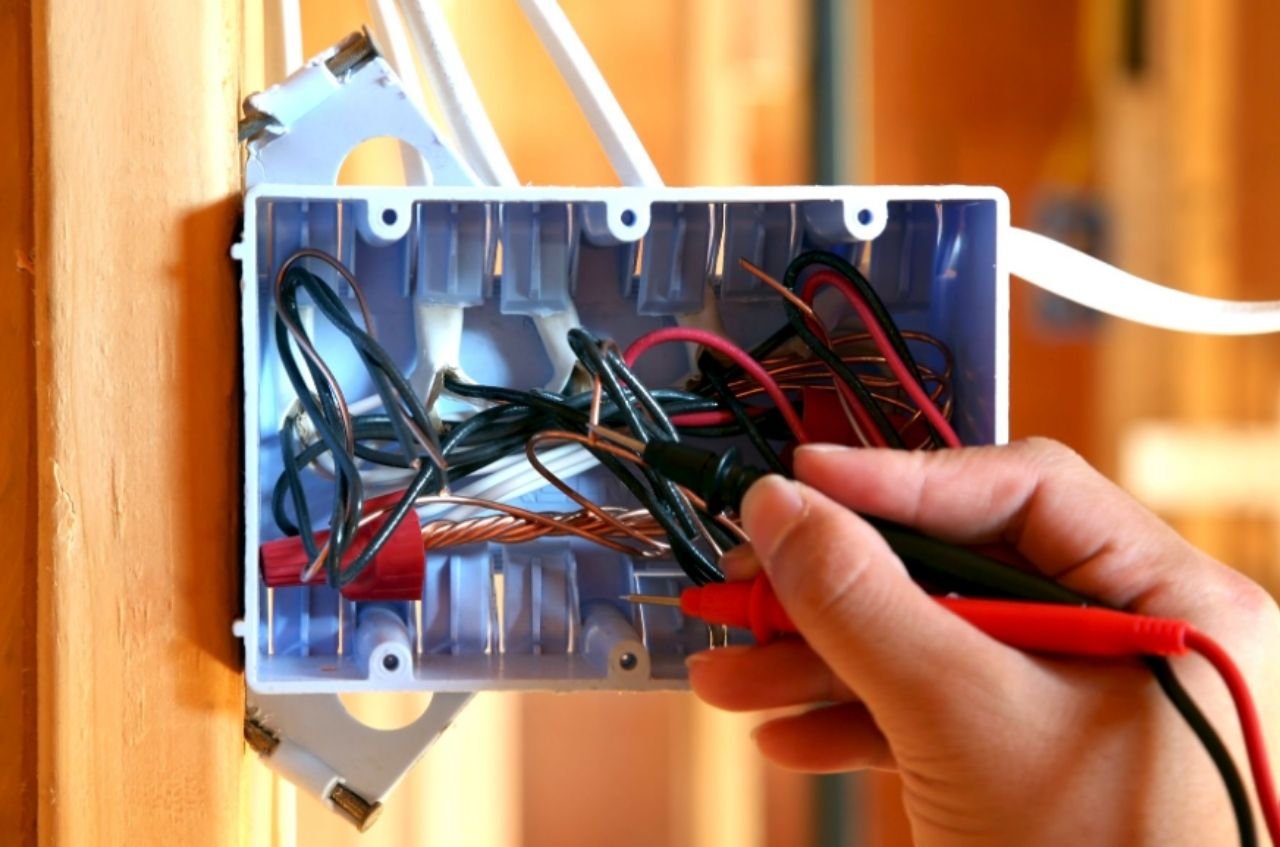
Requirements for Connectors and Fittings
Connectors and fittings should be compatible with type and size of conduit or cable used. They should be tight and secure so that they do not allow moisture or some contaminants to get into the junction box.Sealing and Protection Standards
Securing the entries is important to shield the electrical connections from external elements. Metal parts and other components can be sealed with weatherproof fittings and gaskets in case the device is to be installed outside or in a humid climate.Compliance and Inspection
Importance of Adhering to NEC Codes for Junction Boxes
It is crucial to follow NEC codes to minimize electrical risks and prevent legal issues. Following these standards minimises the chances of electrical risks and provides for safe electrical works and installations.Typical Inspection Process for Junction Boxes
The following is a common sequence of steps followed during the inspection of junction boxes at a construction site. The inspections are carried out to ensure conformity to NEC specifications. Some of the things checked include proper installation, proper grounding, correct box size, proper covers among other things.Common Violations and How to Avoid Them
Some of the most frequent offenses are the use of improper size of the boxes, wrong grounding, and inadequate spacing. They can be prevented by adherence to NEC provisions, standard and proper installation methods, and certified materials.Updates and Changes in Recent NEC Editions
Significant Updates in Recent NEC Editions
Subsequent releases of the NEC have incorporated modifications to enhance safety and incorporate new technologies. Some of these are better grounding requirements, modified box fill factors, and new rules for hazardous areas.Impact of These Changes on Junction Box Requirements
The changes affect the specifications of junction boxes and require adherence to current standards. Electricians need to be aware of such changes to be able to perform installations that are safe and conforming to the current requirements.Practical Tips for Electricians
Best Practices for Complying with NEC Standards
Adhere Strictly to NEC Guidelines:
You should always follow the specific instructions and requirements of the NEC. This makes certain that all the electrical installations are in compliance with the minimum safety standards hence minimizing the risk factors.Use Approved Materials and Equipment:
Always choose materials and equipment which are certified and recommended for their intended use. This encompasses the choice of junction boxes, connectors and fittings that are NEC compliant for the expected environment and electrical current.Ensure Proper Grounding:
Junction box grounding requirements is essential for avoiding electrical shocks and fire accidents. All metal parts should be properly grounded and the grounding conductors should be properly sized and connected well. Refer to NEC 110.26 for details on grounding procedures.Maintain Adequate Clearance:
Electrical box clearance requirements states that spaces around junction boxes and other electrical parts conform to the NEC Section 110.26. This includes clear width of not less than 30 inches and clear junction box height from floor of not less than 36 inches and a minimum headroom clearance of two and half feet.Engage in Regular Training and Updates:
Continue to read the updated versions of the NEC by attending training sessions, seminars or workshops. Subsequently, continuous education keeps electricians abreast of new standards, technological advancement, and safe practices, making it continuous.Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Using Undersized Junction Boxes:
The first mistake that people make is getting junction boxes that are not large enough to accommodate the quantity of conductors and the devices. This in turn results in overheating, short circuit formation and high chances of fire outbreak. Remember to always determine the correct box size as per NEC Section 314. 16, taking into account the amount needed for all parts of the recipe.Neglecting Grounding Requirements:
Not grounding electrical installations effectively is a severe danger. Check that all the metallic interfaces such as the junction boxes and conduits feature effective grounding. In this aspect, ensure that you use the correct grounding methods, as recommended by the NEC to help you avoid electrical shocks and fires.Installing Junction Boxes in Inaccessible Locations:
Ideally, junction boxes should be easily accessible for purposes of maintenance, inspections and even repairs. Do not place boxes in blind or elusively located locations because access can prove challenging in the future and new problems can go unnoticed. NEC section 29 to allow for proper access to the premises.Overcrowding Wires and Devices:
Do not cram lots of wires and gadgets in a single junction box to save time and efforts. In particular, overcrowding causes deficient insulation, high temperatures, and short circuits. Determine proper box fill and verify that adequate room exists for all conductors and devices according to NEC Section 314.Improper Use of Connectors and Fittings:
You need to avoid substandard fittings and connectors in electrical practices due to their poor quality and workmanship. Make sure all connectors and fittings match the conduit/cable type and give a positive secure connection that will not allow moisture or mechanical stress to penetrate. Comply with the NEC regulations regarding conduit and cable entries.Conclusion
You must follow NEC junction box code to maintain electrical safety and avoid risks. It is important to install junction boxes correctly and learn about the electrical junction box rules and guidelines to prevent electrical hazards. This article focused on the NEC, requirements for junction box material, minimum volume size, use of hazardous or non-hazardous areas, grounding and clearances, covers, conduit and cable entries, and how to conduct inspection on junction boxes. It also pointed to recent changes and useful advice for electricians. Electrical safety means following NEC codes, using qualified products, and other necessary measures. Correct application of junction boxes is pivotal in ensuring that electrical systems do not pose a threat to human life and property hence is of significant importance.


