Metal Surface Finishing: What You Should Know

Table of Contents
ToggleIs your metal surface rusty and seasoned? This not only reduces their value as art but also leads to their deterioration. This is because the imperfections if not addressed may result in expensive replacements and repairs. Fortunately, metal surface finishing has a way out. With the knowledge of the techniques and the advantages of each, you’ll be able to revitalize your metal and give it more years of service.
Understanding Sheet Metal Finishing Techniques
Sheet metal finishing involves the application of methods and treatments to enhance the surface of metal components aiming to improve their functionality, durability and visual appeal. To achieve desired qualities these finishing techniques utilize chemical or mechanical processes. The applications of metal surface finishing are diverse ranging from enhancing resistance, to corrosion and environmental factors to improvements.
The Importance of Surface Finish for Sheet Metal Parts
Surface finishing of sheet metal components serves purposes. It enhances the appearance by creating an appealing look. Moreover surface treatments act as a barrier against oxidation, corrosion and wear thereby increasing the durability of metal parts. Coatings can also enhance surface hardness reduce friction and provide properties such as conductivity or insulation. These treatments play a role, in extending the lifespan of sheet metal parts. Ensuring they meet specified usage requirements by enhancing both their appearance and functionality.
Metal Surface Finishing Techniques
Bead Blasting
Bead blasting is a method that utilizes glass beads or similar abrasives to cleanse and refine metal surfaces resulting in a matte finish by eliminating surface impurities and flaws.

Advantages
- Creates a matte finish.
- Eliminates surface. Flaws.
- Enhances surface adhesion, for coatings.
Disadvantages
- May be abrasive potentially weakening metals.
- Requires equipment.
Applications
- Commonly used in the aerospace and architectural sectors.
- Ideal for finishes. Preparing surfaces for painting or coating.
Recommended Metals for Bead Blasting
- Aluminum
- steel
- Titanium
- Stainless Steel
Anodizing
Anodizing is a metal surface finishing technique that transforms metal surfaces into a corrosion resistant anodic oxide finish frequently applied to aluminum components.

Advantages
- Improves corrosion resistance properties.
- Provides a surface.
- Available in color options.
Disadvantages
- Limited to metals, aluminum.
- Can be relatively costly compared to finishing methods.
Applications
- Widely used in aerospace, automotive and consumer electronics industries.
- Suitable for parts exposed to environments.
Recommended Metals, for Anodizing;
- Aluminum
- Titanium
Magnesium Powder Coating
Powder coating is the process of applying a powder onto a metal surface. Then baking it at high temperatures to create a strong and long lasting finish. It is popular, for its durability and the wide array of colors it offers.

Pros
- Produces a tough finish.
- Offers a selection of colors and textures.
- Environmentally friendly with emissions of organic compounds (VOCs).
Cons
- Requires high temperature curing.
- Challenging to achieve coatings.
Commonly Used in
- Automotive, furniture and appliance industries.
- Ideal for applications due to its resilience.
Recommended Metals
- Aluminum
- Steel
- Iron
Electroplating
Electroplating is the process of using a current to deposit metal ions onto an electrode forming a cohesive metal coating. It enhances metal surface finishing and provides protection against corrosion.
Advantages
- Provides resistance against corrosion.
- Can improve conductivity.
- Offers finishing options.
Disadvantages
- Involves handling chemicals.
- Necessitates control, over the plating procedure.
Commonly Applied in
- Electronics, automotive and jewelry sectors.
- Well suited for both functional coatings.
Recommended Metals
- Copper
- Nickel
- Gold
Electrophoretic Coating Overview
Electrophoretic coating, also known as e coating is a method of applying a coating using a current. This process ensures a thickness of the coating. Is considered environmentally friendly.
Advantages
- Provides consistent coating thickness.
- Offers adhesion and resistance to corrosion.
- Environmentally friendly, with waste production.
Disadvantages
- Requires equipment and setup.
- Limited to use on conductive materials.
Applications
- Widely used in the appliance sectors.
- Particularly suitable for shapes and components.
Recommended Metals
- Steel
- Aluminum
- Zinc
Dacromet Description
Dacromet is a water based coating that delivers corrosion resistance by combining zinc and aluminum flakes within a binder. It is typically applied through dip spin or spray methods.
Advantages
- Superior corrosion protection.
- Creates a coating.
- Exhibits heat resistance properties.
Disadvantages
- choice of colors
- Contains substances classified as materials.
Applications
- Commonly utilized in the construction industries.
- Ideal, for fasteners, clamps and brackets.
Recommended Metals
- Steel
- Iron
- Zinc
Passivation Overview
Passivation involves treating steel with an acid solution to eliminate free iron particles from the surface. This process enhances its resistance to corrosion by forming a protective oxide layer.
Advantages
- Improves resistance, to rust.
- Cleans off surface dirt.
- Safe for the environment and non
Disadvantages
- works on metals, especially stainless steel.
Applications
- Commonly used in aerospace and food industries.
- Great for parts and components made of steel.
Recommended Metals
- steel
Chemical Film Coating
Description; Chemical film coating, also called chromate conversion coating, safeguards aluminum and its alloys from corrosion while creating a base for painting.
Advantages
- Enhances resistance against rust.
- Boosts paint adhesion.
- Applied at room temperature.
Disadvantages
- Limited to metals only.
- Requires handling of chemicals during application.
Applications
- Utilized in aerospace, automotive and military sectors.
- Suitable for aluminum and magnesium alloys.
Best Metals Recommended
- Aluminum
- Magnesium
Electroless Plating
Electroless plating involves depositing a layer of solution containing metal salt and a reducing chemical agent through a reduction process without using a current. This metal surface finishing method ensures even thickness and excellent durability against wear.
Advantages
- Ensures even thickness distribution, on surfaces plated.
- Capable of plating surfaces that are non conductive.
- Excellent resistance to wear.
Drawbacks
- The process is slower compared to electroplating.
- Precise control of the chemical bath is necessary.
Applications
- Commonly used in electronics, and industrial sectors.
- Ideal, for shaping forms and surfaces.
Recommended Metals
- Nickel
- Copper
- Gold
Spraying
The spraying method involves coating a metal surface by using a spray gun to apply a material. This technique allows for the use of materials like paint, powder or liquids to create an decorative finish.
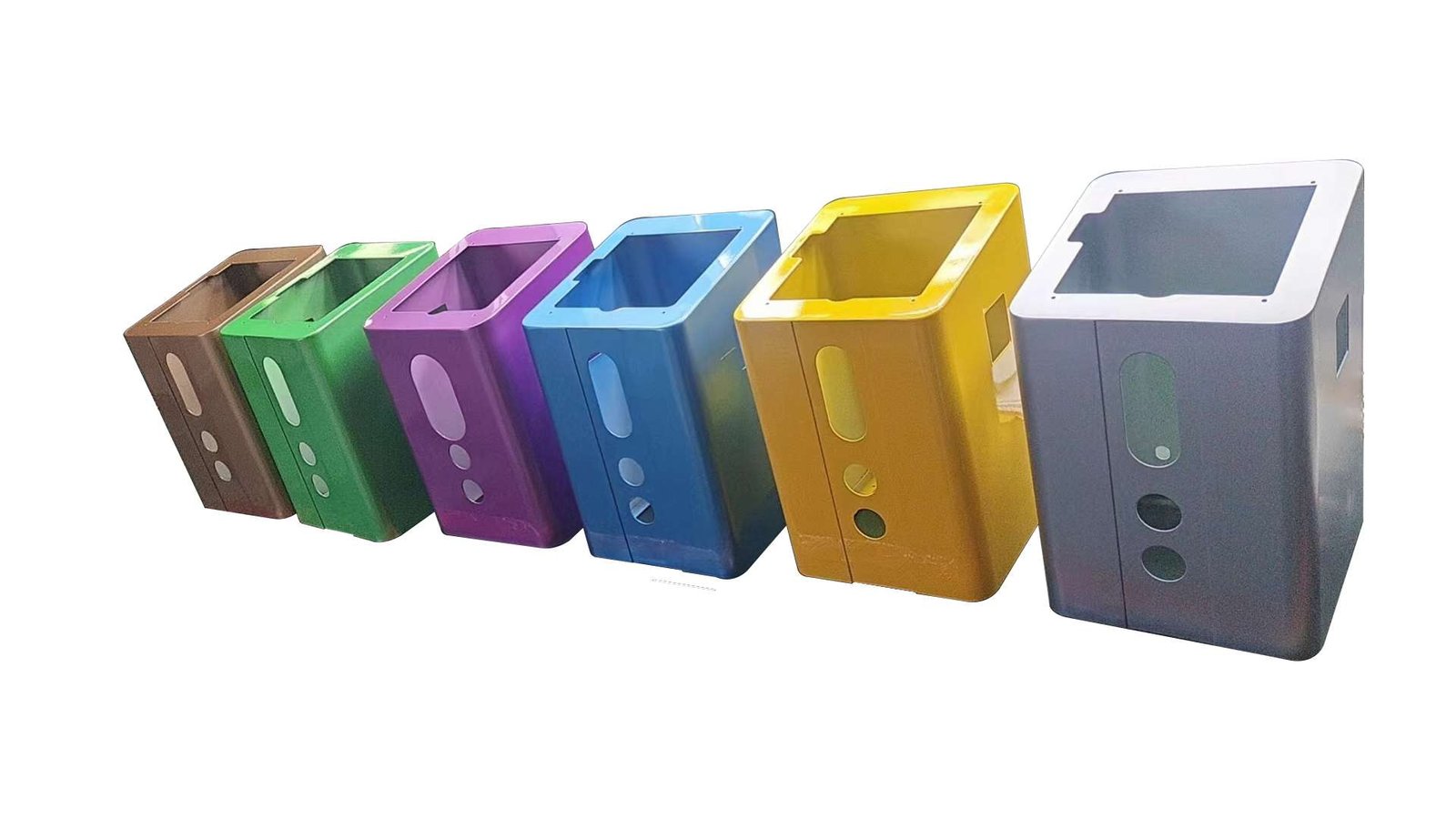

Advantages
- Application methods HVLP, airless, etc.).
- Wide selection of coating materials to choose from.
- Quick application on surfaces possible.
Drawbacks
- Proper ventilation and safety precautions are essential.
- Overspray may result in wastage.
Applications
- Utilized in construction and furniture industries.
- Suitable for both decorative coatings.
Recommended Metals
- Steel
- Aluminum
- Iron
Galvanizing
Galvanizing is the process of adding a zinc coating to steel or iron surfaces to prevent rusting. Typically done by immersing the metal in molten zinc to create a layer that resists corrosion effectively.
Advantages
- resistance against corrosion.
- Cost effective, for protecting structures.
- Provides long term protection.
Cons
- May result in a surface texture.
- Limited range of color choices.
Usage
- Widely seen in the fields of construction, automotive and marine sectors.
- Particularly suitable, for steel structures, pipelines and outdoor use.
Recommended Metals
- Steel
- Iron
Dip Coating
Hot dip coating is akin to galvanization. May involve alternative metals such as aluminum or tin. The process entails submerging the metal into a bath to create an resilient coating.
Pros
- Offers a durable coat.
- defense against rust and corrosion.
- Appropriate for intricate structures.
Cons
- Demands high processing temperatures.
- Can yield a surface finish.
Usage
- Applied in the realms of construction, automotive and utility sectors.
- Well suited for applications and outdoor frameworks.
Recommended Metals
- Steel
- Iron
Electrochemical Polishing (Electropolishing)
Electropolishing eliminates a layer of material from a metal surface through a method resulting in a sleek lustrous appearance.
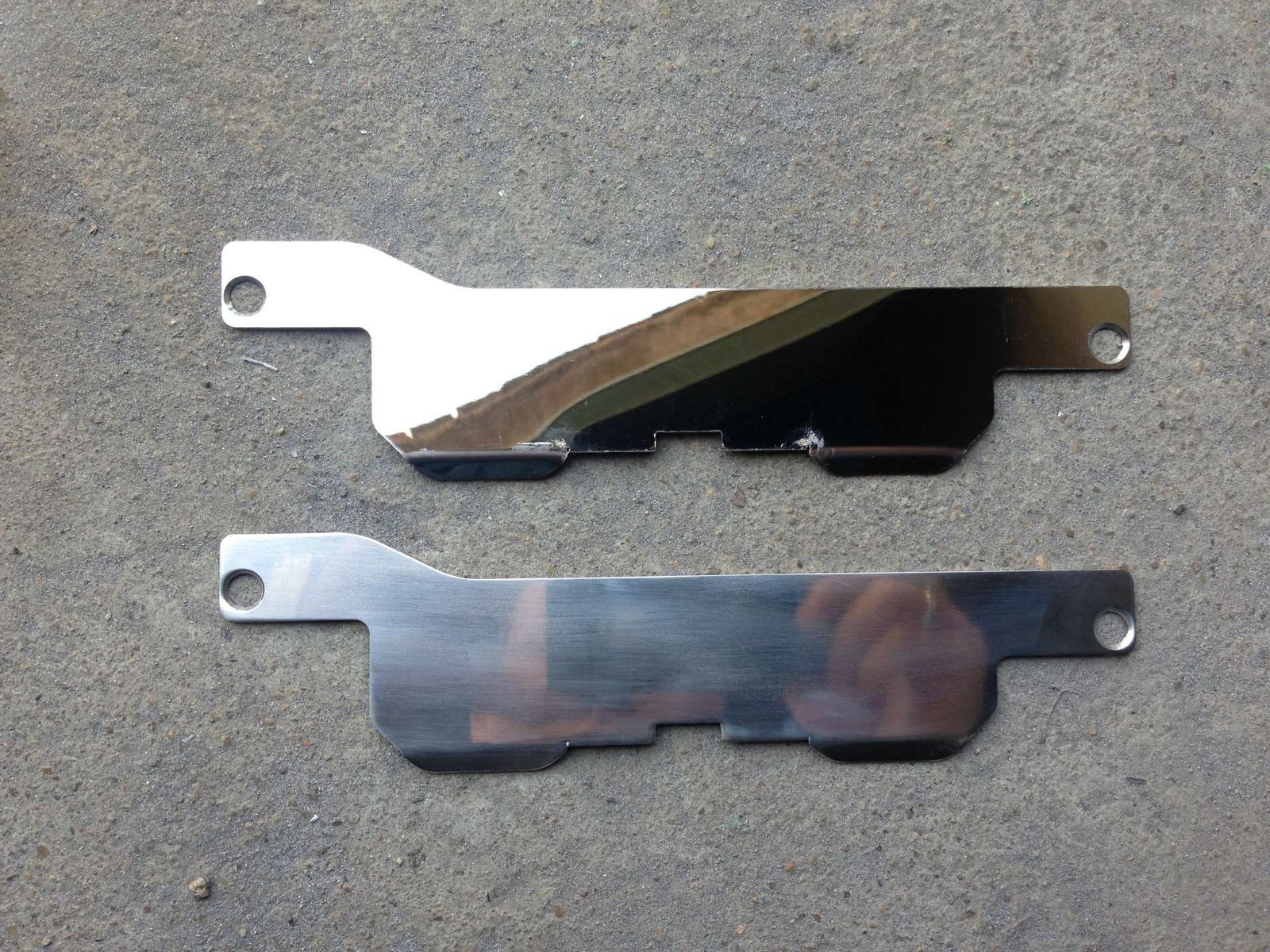

Pros
- Yields a sleek and lustrous metal surface finishing.
- Enhances resistance to corrosion.
- Eliminates surface.
Cons
- Requires machinery.
- Applicable solely, to metals.Industries where this is used include pharmaceutical and food processing.
Great, for
- steel and precise components.
- Top metals to consider are steel, aluminum and titanium.
Black oxide coating
It gives a finish to iron based metals offering some corrosion protection and reducing reflection.

Advantages include
corrosion resistance improved appearance with a finish and decreased light reflection.
Drawbacks are
- limited to iron based metals.
- The need for post treatment with oil or wax for protection.
- This method is common, in automotive, firearms and tooling sectors.
- It works well with steel parts.
Recommended metals are
steel and iron.
Cladding
Cladding is a process where one metal layer is bonded to another to combine their properties, such, as improving corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. It can also enhance surface characteristics.
Advantages of cladding include
corrosion resistance, improved properties and the ability to blend the characteristics of different metals.
Drawbacks
However it may come with drawbacks like being costly and requiring equipment.
Applications
This technique finds applications in industries like aerospace, automotive and construction for components. Metals like aluminum, stainless steel and titanium are commonly used for cladding.
Coating
Moving on to hard coating methods achieved through processes like anodizing or plasma electrolytic oxidation – they creates metal surface finishing that resist wear effectively while boosting corrosion resistance and withstanding high temperatures.
The benefits of coating
Include providing a wear resistant surface that can endure high temperatures while enhancing corrosion resistance. On the side this method may be limited to metals and could be costly.
Applications
Hard coating is widely utilized in aerospace, automotive and tooling industries for high wear components and machinery parts.
Preferred metals
suitable for hard coating applications are aluminum, titanium and stainless steel.
Phosphate coating
It involves applying a layer, on steel or iron surfaces to safeguard them against corrosion.
This special coating helps prevent rust makes things slide easier and makes paint stick better.
Pros;
- Stops rust.
- Makes things slide smoother.
- Helps paint stick better.
Cons;
- Only works on metals.
- You have to be careful, with the chemicals.
Where to Use It
- Cars, guns and machines.
- Works best on steel and iron.
Recommended Metals
- Steel
- Iron
Zinc Nickel Plating
Description; Zinc nickel plating coats metals like steel, aluminum and iron with a mix of zinc and nickel. This coating is great at stopping rust and wear, perfect for conditions.
Pros
- Great at preventing rust.
- Resists wear well.
- Can be used for decoration.
Cons
- Costs than zinc plating.
- Needs precise control during the coating process.
Where to Use It
- Automotive, aerospace and electronics industries.
- Perfect for parts in conditions.
Recommended Metals
- Steel
- Iron
- Aluminum
Vibratory Finishing
Vibratory finishing smooths out metal surfaces by putting them in a vibrating container, with material. This method smooths out edges removes imperfections and gives surfaces a look.
Benefits
- Enhances the smoothness and shine of surfaces.
- Can handle volumes of parts at once.
- Eliminates edges and sharp points.
Drawbacks
- Requires tools.
- Suitable, for parts.
Applications
- Commonly used in the aerospace and jewelry sectors.
- Ideal for components needing a finish.
Recommended Metals
- Steel
- Aluminum
- Brass
Drum Plating
Description; Drum plating involves placing metal parts in a rotating drum filled with plating solution and metal ions. The parts roll inside the drum ensuring a coating application.
Advantages
- Efficient, for processing a number of parts.
- Ensures uniform coating application.
- Cost effective option.
Disadvantages
- Limited to components.
- Risk of parts getting tangled during the process.
Applications
- Used in manufacturing, electronics production and fastener industries.
- Preferred for screws, bolts and small hardware items.
Recommended Metals
- Steel
- Brass
- Copper
Buffing Process
Description; Buffing employs spinning cloth wheels with substances to smooth and enhance the sheen of metal surfaces. It is commonly employed for improvements.
Benefits
Produces a finish that enhances appeal.
Applications
- This technology is utilized in the aerospace and tool industries.
- It is most effective, for crafting gears, springs and cutting tools.
Recommended Metals
- Steel
- Aluminum
- Titanium
Laser Engraving for Metal Surface Finishing
Explanation; Laser engraving involves using a laser beam to eliminate material from the surface of metal resulting in designs, logos or text. It offers precision and lasting results.
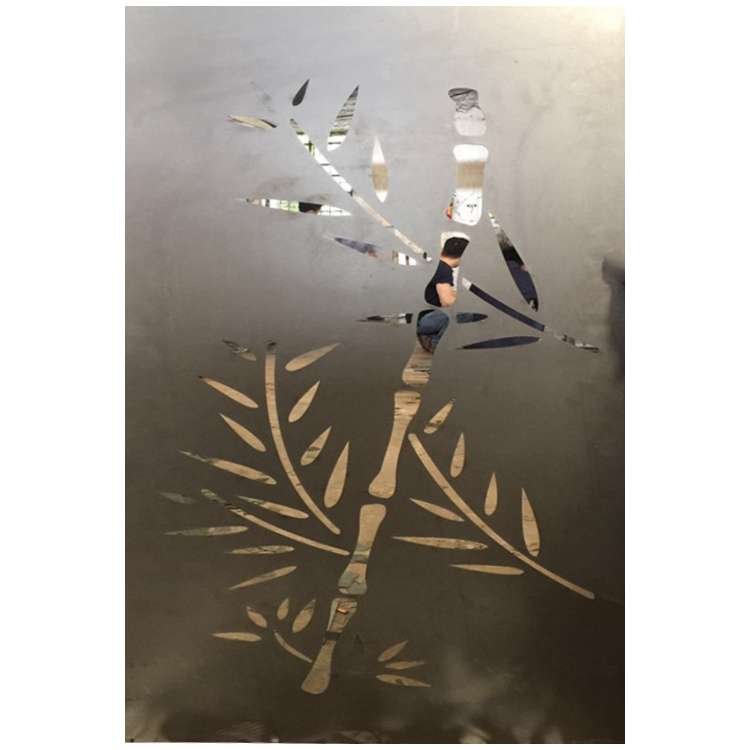

Advantages
- precision and intricate detailing.
- Permanent markings that endure over time.
- A non invasive process that doesn’t require contact.
Disadvantages
- Investment in equipment required.
- Limited to marking surfaces
Applications
- This technique finds applications, in jewelry making, electronics manufacturing and industrial marking processes.
- It is particularly well suited for etching numbers, barcodes and logos onto surfaces.
Recommended Metals
- steel
- Aluminum
- Brass
Shot Peening
Shot Peening is a process that bombards metal surfaces with media to induce compressive stress enhance fatigue resistance improve surface finish and reduce stress corrosion cracking.

It provides benefits
like fatigue resistance enhancement and surface finish improvement.
Requires equipment for specific applications
in industries such as aerospace, automotive and tooling. It is commonly used for creating gears, springs and structural components
using metals,
like steel, aluminum and titanium.
Teflon Coating
It involves applying Teflon to surfaces to provide stick properties or corrosion resistance.Teflon coating is the process of applying a layer of PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), on metal surfaces to create a stick low friction finish that offers excellent resistance to chemicals.
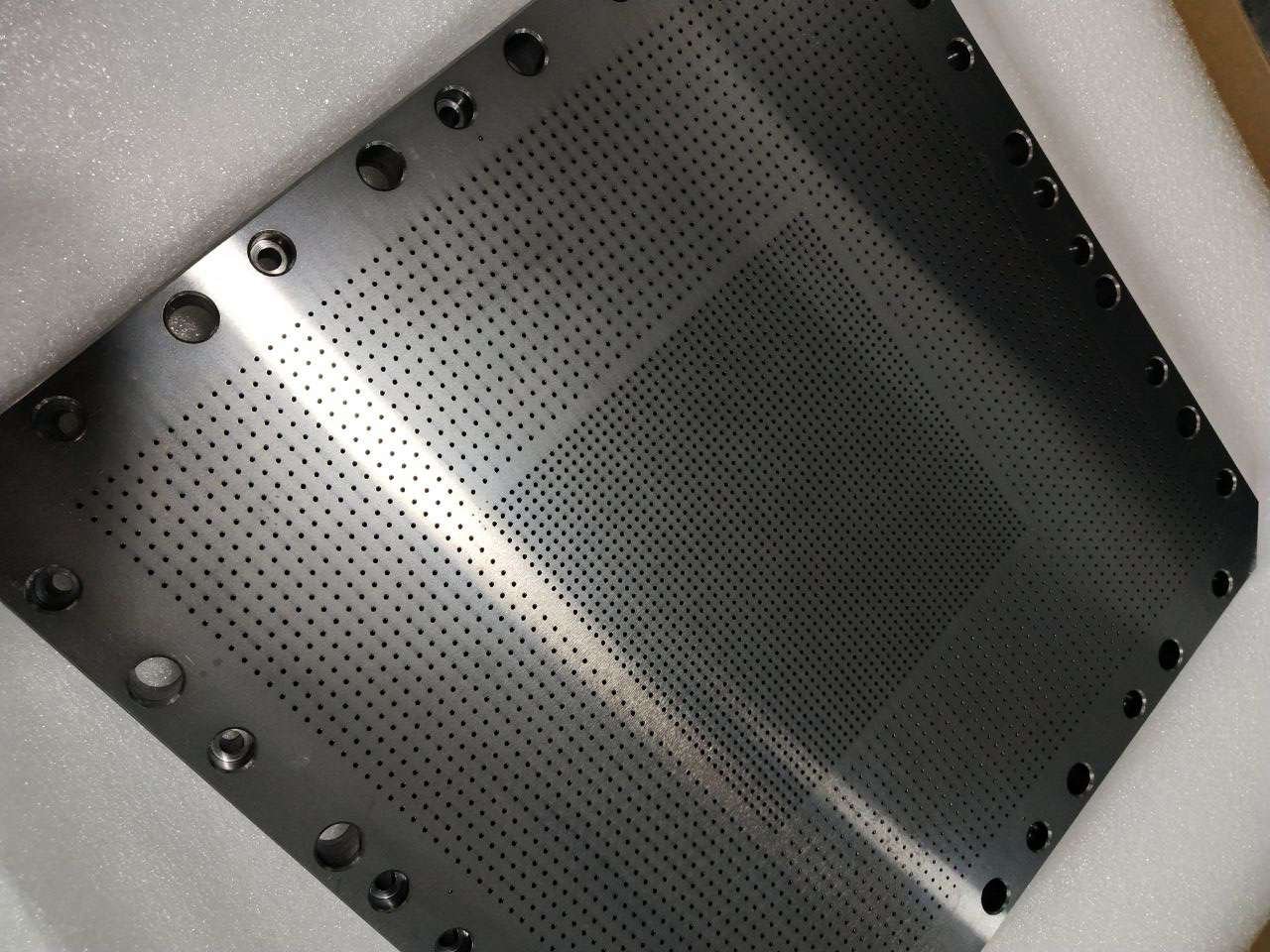

Advantages
- stick properties and low friction.
- Excellent resistance to chemicals.
- Ability to withstand temperatures.
Disadvantages
- Can be costly.
- Requires control during application.
Applications
- Commonly used in cookware, automotive and industrial settings.
- Well suited for bearings, valves and cookware.
Recommended Metals
- Steel
- Aluminum
- steel
Thermal Spraying
Description; Thermal spraying involves heating and propelling coating materials onto metal surfaces to form a layer. This method supports the use of coating materials such as ceramics, metals and polymers.
Advantages
- Versatility in coating material options.
- Provides durable coatings that enhance wear and corrosion resistance.
Disadvantages
- Specialized equipment is necessary for spraying.
- Proper surface preparation is crucial for effectiveness.
Applications
- Widely utilized in aerospace, automotive and industrial equipment sectors.
- beneficial, for turbine blades engine. Protective coatings.
Recommended Metals
- Steel
- Aluminum
- Titanium
Vibratory Deburring
Overview; Vibratory deburring involves using a vibrating container filled with media to smooth out metal parts by removing burrs, sharp edges and surface imperfections. This is an effective metal surface finishing technique.
Advantages
- Efficient for processing in bulk.
- Eliminates burrs and sharp edges.
- Improves the surface finish of the parts.
Disadvantages
- Requires equipment for operation.
- Suitable for small to medium sized parts.
Applications
- Applied in aerospace and manufacturing sectors.
- Particularly useful for deburring, polishing and refining components.
Recommended Metals
- Steel
- Aluminum
- Brass
Polish Quench Coating
It, is also known as QPQ Coating and A surface treatment known as QPQ coating involves immersing the metal in a bath of salt polishing it and then immersing it again.

Advantages
This process results in a coating that’s resistant, to corrosion and wear on the metals surface.
Disadvantages
One flaw is a lack of material compatibility and the second one is difficulty in controlling and reproducibility. this process needs regular monitoring and checking which makes it more challenging and tough to operate.
Uses
QPQ coating is commonly applied to items such as firearms, gears and vehicles that require durability. It is applied in the gas industry, defense, and medical industries. Some of its uses are found in power transmission tools and hydraulic components.
Recommended metals
- cast iron
- tool steel
- low carbon steel
Nitriding in a Salt Bath
By introducing nitrogen into the surface of the metal through a method called salt bath nitriding. The metal is placed in a salt solution containing nitrogen compounds to facilitate this process.
Advantages
the hardness, fatigue strength and wear resistance of the metal are all enhanced.
Defects
- need high temperature
- thermal stress and deformation are results of high-temperature
Uses
In industries like tooling, automotive manufacturing and aerospace engineering this treatment is widely utilized for steel. Cast iron components.
Recommended metals
- sintered iron
- cast iron
- steel
PVD Coating
When it comes to PVD coating the process involves applying layers of material onto a metal surface, within a vacuum environment.
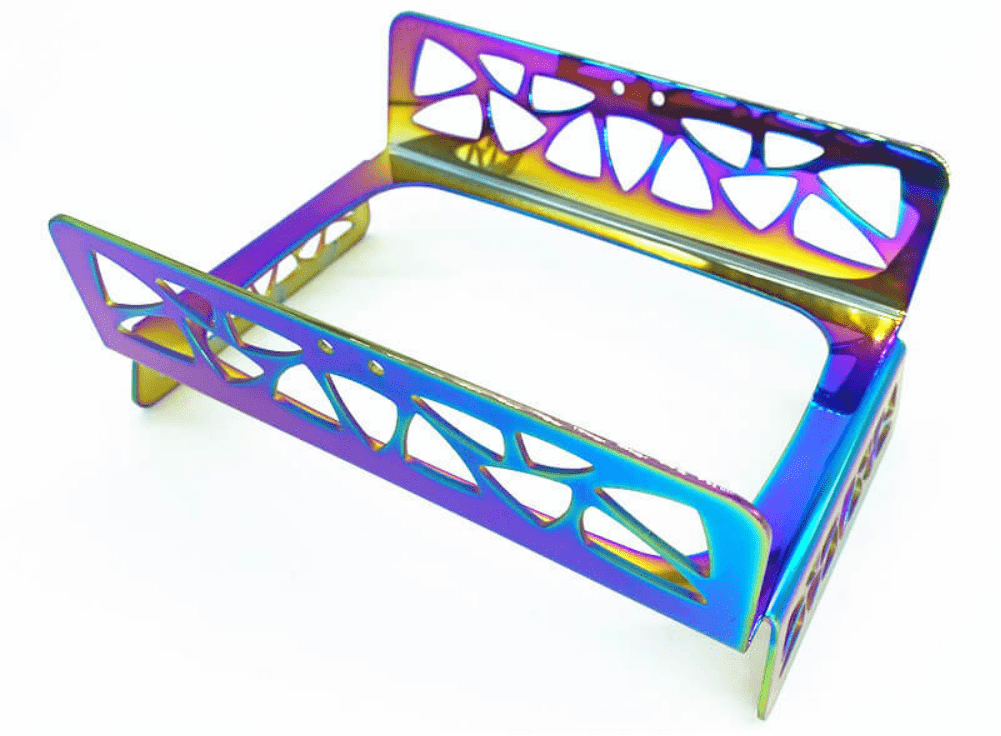

Benefits
This method results in a visually appealing finish. The exceptional hardness and aesthetic appeal of PVD coatings make them highly sought after in industries.
Flaws
- scratches
- partial color difference
- visible babble appear
Where to use it
- like jewelry,
- automotive
- tool manufacturing.
Recommended metals
- aluminum
- copper
- stainless steel
Brushed Satin
A satin or brushed finish achieved through treatment gives metal surfaces a texture that is not reflective. This effect is created by brushing the metal with a substance to form parallel lines.

Benefits
The satin finish is popular due to its look.
Flaws
more susceptible to tea staining and contamination
Where to use it
In architectural projects, household appliances and automotive trim.
recommended metals
Is commonly used on metals like aluminum stainless steel,
Reason for choosing a metal surface finish
It is essential to apply a surface finish to sheet metal components for reasons, such as enhancing aesthetics boosting functionality and increasing longevity. Here are the key rationales behind adding a surface finish to sheet metal parts;
Protection Against Corrosion
Explanation; Certain metals are susceptible to corrosion when exposed to challenging conditions. Surface finishes act as shields against moisture, chemicals and other corrosive agents.
Benefits; Prolongs the lifespan of the metal part reduces maintenance expenses. Prevents damage caused by corrosion.
Enhanced Visual Appeal
Explanation; Surface finishes can elevate the attractiveness of metal parts making them more appealing and suitable, for consumer oriented uses.
Enhancing the desired look boosting product appeal and staying true, to the brands style or design guidelines are aspects to consider.
Toughness
Explanation; Certain surface treatments toughen metal surfaces shielding them from scratches, dents and other types of wear and tear.
Advantages; Extends the lifespan of the component preserves its functionality and lowers the risk of damage during usage or handling.
Electrical Efficiency
Explanation; Specific treatments like electroplating can. Sustain the conductivity of metal components crucial for electronic devices.
Advantages; Ensures performance reduces resistance at contacts and enhances signal transmission.
Heat Transfer Capability
Explanation; Some treatments can boost the heat transfer capacity of metal components for dissipating heat in electronics and machinery.
Advantages; Enhances thermal management, prevents issues. Optimizes thermal system efficiency.
Preparing Surfaces for Subsequent Procedures
Explanation; Treatments ready metal surfaces for procedures like painting, bonding or welding, by improving adhesion and consistency.
Advantages; Guarantees quality and longevity of coatings or adhesives resulting in more dependable products.
Minimizing Friction
Explanation; surface treatments like the application of Teflon coating help reduce friction, between metal components, useful in machinery with moving parts.
Advantages; Improves the efficiency of systems lessens wear and tear and reduces energy consumption.
Protection Against Chemicals
Explanation; Utilizing coatings can shield metal parts from chemical damage crucial for environments exposed to substances like acids and bases.
Advantages; Enhances the parts resilience to chemical deterioration ensuring durability and reliability in conditions.
Cleanliness and Sanitation
Explanation; Smooth and impermeable finishes facilitate cleaning and disinfection processes, important in industries such as healthcare, food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Advantages; Upholds stringent hygiene standards, prevents contamination risks and complies with standards.
Preventing Oxidation
Explanation; Metal surface finishing techniques like anodizing can forestall metal oxidation issues seen in materials like aluminum that can impact both aesthetics and performance.
Advantages; Preserves the integrity of the averts discoloration concerns while sustaining functionality.
Personalization Options for Brand Identity
Explanation; Surface treatments offer opportunities for customization through choices, in color palette texture variations or unique patterns to effectively establish a ccompanybrand image.
Differentiating products, in the market reinforcing brand identity and meeting customer preferences are aspects. Applying a surface finish to sheet metal components is a decision that improves their functionality, appearance and lifespan making them suitable for applications across diverse industries.
Guidelines for Choosing a Sheet Metal Finish
Selecting a sheet metal finish involves considering factors to ensure that the chosen finish meets the aesthetic and economic needs of the particular application. The selection process commences with understanding the purpose of the finish. For example if corrosion resistance is a requirement finishes like anodizing, galvanizing or powder coating may be choices. These finishes offer protection against elements ensuring the durability and longevity of the metal components.
How much important is to understanding the factors crucial when deciding on the surface treatment?
When choosing surface finishes for metal components it’s important to consider application factors along, with the specific characteristics of the metal itself. This process requires an evaluation focusing on achieving desired end goals.

Consider the Application Requirements
The first step in selecting a metal surface treatment is to understand the needs of your application. Components exposed to chemicals, moisture or harsh conditions require corrosion resistance, which can be achieved through finishes like powder coating, galvanizing or anodizing. For parts subjected to wear or friction enhancing surface hardness and durability can be accomplished with finishes such as spraying, nitriding or hard anodizing. To achieve appeal with a variety of color options finishes like polishing buffing and anodizing are ideal. Electronic components necessitate conductivity; hence gold or silver electroplating is a choice. Finishes like spraying or specialty coatings provide conductivity, for applications requiring specific thermal properties.
Consider the Base Metal
Different metals react uniquely to finishing techniques; it is crucial to select a finish that complements the base metal appropriately. For instance aluminum is often treated with anodizing, powder coating and chemical film coating.

Stainless steel can benefit from processes like bead blasting, electropolishing, passivation and nitriding while steel is often treated with galvanizing, electroplating and powder coating. When it comes to copper and brass common metal surface finishing techniques include lacquering, electroplating and electroless plating. It’s crucial to ensure the base metal and the finish complement each other for the results.
Consider Environmental Factors
The environment in which a metal part operates plays a role, in choosing the finish. For parts exposed to conditions requiring weather resistance finishes like powder coating, anodizing and galvanizing are essential. In settings where corrosion resistance’s critical options like Dacromet, hot dip galvanizing or marine coatings tailored for specific needs are ideal. In situations involving chemical exposure protection can be provided by plating, passivation or certain chemical resistant coatings.
Evaluate Functional Needs
The functional requirements of a part also impact the choice of finish because some finishes can significantly alter dimensions and tolerances. Processes like electroplating and powder coating may affect tolerances. Have less impact on dimensions compared to electropolishing and passivation. Finishes that enhance adhesion such, as film coating or bead blasting can be beneficial if further painting or bonding is required for the item.
Buffing or electropolishing can help achieve the desired smoothness and cleanliness, for applications that demand a level of finish.
Consider Cost and Efficiency in Production
When deciding on a surface finish practical considerations such as manufacturing constraints and budgetary concerns come into play. Some finishing methods, like gold electroplating and PVD coating may be more expensive. Offer qualities. For applications anodizing and powder coating are cost processes. Another factor to consider is production time; thermal spraying and electroless plating may require time compared to electroplating and passivation which’re quicker processes.
Adherence to Regulatory Standards and Industry Guidelines
It is essential to ensure that the chosen finish complies with industry regulations and standards. For instance coatings used in the aerospace industry must meet performance and durability criteria. Medical equipment must adhere to standards for biocompatibility and cleanliness making passivation and electropolishing choices. Finishes in the sector should be visually appealing while being resistant to wear and corrosion.
Seek Advice from Professionals
Engage with material scientists, engineers or finishing experts, for guidance when uncertain. These professionals possess knowledge and technical expertise that enable them to assess your projects needs effectively and recommend optimal finishing solutions.
The wide range of surface metal finishing methods allows for customization of metal components to meet functional and aesthetic requirements. It is crucial to select the finishing technique based on the intended usage desired characteristics and surrounding conditions.
In summary
Sheet metal finishing encompasses an array of procedures and techniques aimed at enhancing the appearance, durability and functionality of metal components. Each technique offers benefits and applications including PVD coating, printing, bead blasting and anodizing. Familiarity, with these metal surface finishing methods empowers manufacturers to choose the suitable approaches, for their specific needs ensuring that metal components not only look appealing but also possess the strength required to withstand their intended applications. Careful selection and application of surface treatments can significantly enhance the longevity and performance of sheet metal elements.
By employing finishing processes manufacturers can achieve optimal quality standards while enhancing the performance, durability and visual appeal of their metal components.



