

+86-18969433502
sales@sheetmetalmasion.com
Over 400+ Employees

7+ Million Production Capacity
30,000 m3 Total Factory

We pride our selves in sheet metal design for manufacture. Our team improves all parameters of your product, its stability, reproducibility, and price. We closely align ourselves with your objectives of enhancing production and cutting unnecessary expenses. Since we work with your designs, we save you money by minimizing the need to make changes at a later date. You can rely on our experience to enhance your designs and prepare them for manufacturing.
Sheet Metal Design

With our wide range of prototyping services, you can easily test and finalize your designs in no time. We do 3D Printing, Laser sintering, CNC machining and vacuum molding. These methods help to evaluate the possibility of a product’s features and function and how well it fits before mass production. Using rapid prototyping you are able to correct errors on early stages, which will be beneficial in terms of time and money. Our team assists to identify the most suitable method to use when creating prototypes. Our support guarantees you the strength to proceed with your design.
Sheet Metal Prototyping
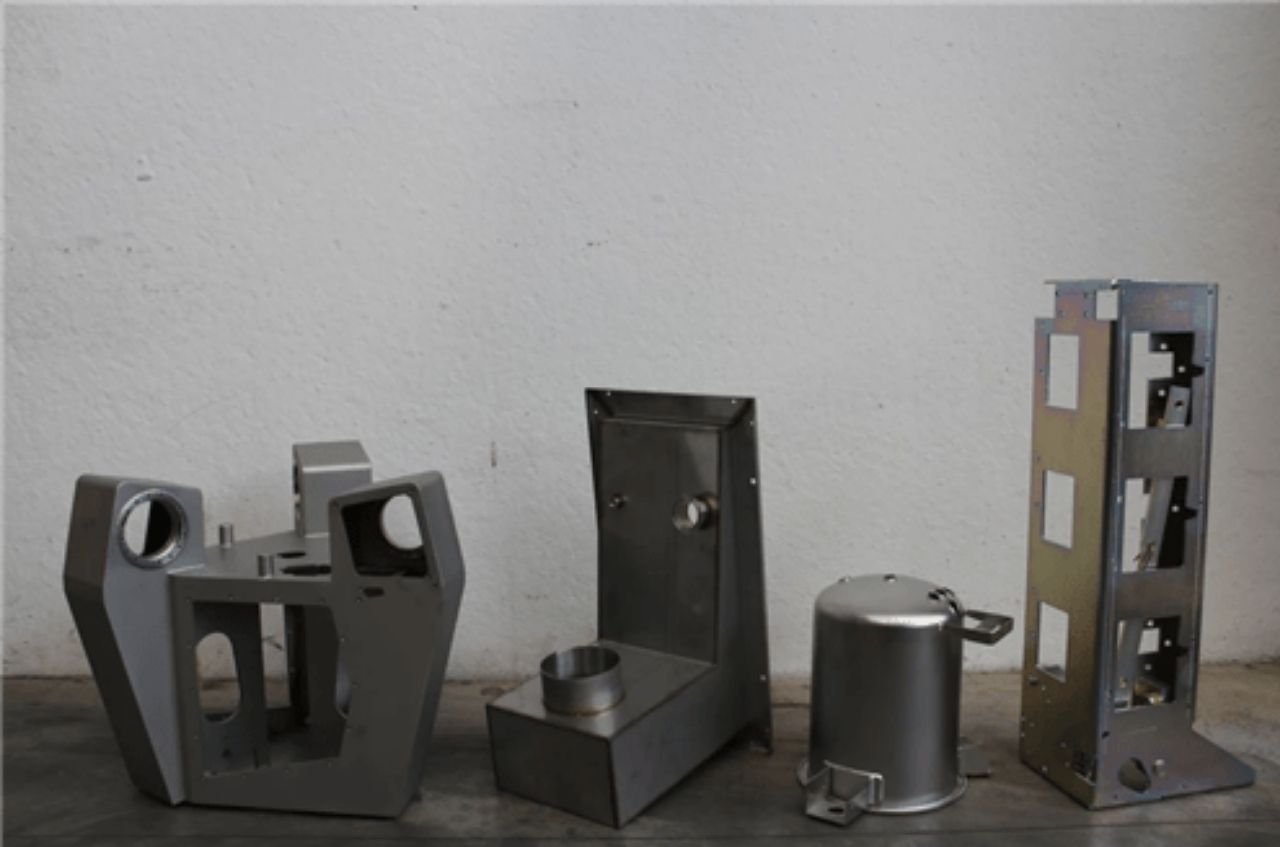

Our pilot production process is comprehensive. Manufacturing problems and defects are diagnosed and fixed. Pilot production is a stage where production processes are optimized, and manufacturing consistency is checked. Our team records and eradicates issues, ensuring that your path to high volume manufacturing is seamless. Problems are detected at an embryonic stage to rectify them before implementation in large scale production. This minimizes time wastage and guarantees that your product is set for the market as soon as possible. Trust us to help you navigate this important stage.
Pilot Productions

We offer detailed product documentation, which is vital to NPI processes. Some of our services include developing electronic BOMs, global drawings, and assembly instructions. Some of the quality tools that we employ include FAIs, PPAP, CpK records, FMEA, and electronic IQC records. Documentation ensures that there is uniformity and accuracy throughout the production process. It also provides a means for communication between your team and our engineers. The documentation we provide also helps you control the production process and minimize the number of mistakes in the finished product. Let us take care of the technicalities as you chart the next big idea.
New Product Documentation

Guide to the New Product Introduction (NPI) Process
NPI New Product Introduction Definition
New Product Introduction (NPI) is a business model that details the efforts required to develop and launch a new product into the market. It involves the entire range starting from the creation of a concept to development and production of the end-product. Concisely speaking, NPI helps a product to be fit for launch into the market eliminating as many risks as possible and at the same time, embracing opportunities for success as many as possible.
Explanation of NPI
NPI plays a central role of verifying that the final product is of the right quality, within required cost and ready for market introduction when required. This structured approach aids in the enhancement of the design, check whether prototypes meet the expected standard, and analyze manufacturability. When done properly, the success of a product and its ability to compete in its respective market, and the reputation of the company can greatly be influenced by an NPI process.
Objectives and Goals
- Targeting cost-efficiency.
- Ensuring higher product quality.
- On time market entry.
The key objectives include:
- Optimizing design.
- Validating prototypes.
- Ensuring manufacturability.
NPI Stages
- Initial Design and Concept
- Design Optimization
- Prototyping
- Pilot Production
- Mass Production
- Product Launch
Importance of NPI
In general, a carefully managed NPI process can provide organisations with a set of significant advantages, such as increased product quality, faster time-to-market and optimised costs. It helps to make sure that a product is fit for production in large quantity to meet market demands and consumers. These result in improved customer satisfaction, superior market positioning, and a more robust corporate image.
2. Initial Concept and Design
Idea Generation
Ideation can be done through brainstroming sessions, conducting surveys about the market and customers. These ideas must be synchronized with current market trends and with the organizational goals and objectives. There are various approaches available in this phase such as SWOT, competitor analysis and customer feedback.
Feasibility Study
A feasibility study entails consideration of the technical, financial, and operational possibilities of the new product notion. These are market analysis to determine customers’ wants, financial analysis to determine potential costs and revenues that can be expected and technical analysis to determine the viability of producing the product.
Design Specification
Detailed design specifications may involve designers, engineers, and other stakeholders as part of the team. Such specifications act as a guideline for the product and describes the characteristics, types of material, sizes, and standards of performance. Comprehensive and unambiguous design documentation is critical for meeting product design and manufacturing requirements.
3. Design Optimization
Design for Manufacturing (DFM)
Manufacturing for Design (MFD) is a process where design decisions are made taking into consideration its manufacture ability. Some of the approaches include the ability to design a simple component, the use of minimal numbers of parts and the choice of cost efficient materials. Specifically, DFM is defined as an endeavor to reduce manufacturing costs and enhance production performance.
Design for Assembly (DFA)
Design for Assembly (DFA) is another concept which directs manufacturing and design efforts towards the ease of assembling a product. This entails the concept that the product should be designed in such a way that it would take little time for it to be assembled besides the cost of assembling it. These principles include reduction of the number of parts making up the product, usage of standard parts in production, and ease of assembling the product.
Iterative Design Process
It is a continuous cycle of designing, developing, and prototyping the product through several stages. While using these systems, feedback is also required so that the processes keep on refining themselves. This also help in identifying problems at various stage of development so that the final designs are optimized and problem free.
4. Prototyping
Prototyping Methods
Different prototyping methodologies are there such as 3D printer, CNC milling machine, and injection method. The specific type of prototyping that will be used depends on the type, structure, materials and funds which are available for the project. Rapid tooling, which is typically based on 3D printing, is ideal for low-run, non-functional prototyping, whereas, high-accuracy functional parts that do not require sweeping interior geometry can be machined from a solid block or molded.
Prototype Testing
Functional and performance tests are performed on a prototype to determine whether design assumptions that have been made during the development are either right or wrong. The need for testing is to confirm the set and expected standards of the product before it is released to the market.
Iteration and Feedback
Subsequent to testing and feedback, prototypes undergo changes in order to improve their feasibility. More frequently, several designs have to be made for the best design to be developed. By using this iterative approach different problems can be found and fixed at an early stage before it requires a lot of changes to be done in mass production.
5. Pilot Production
Setting Up Pilot Production
Pilot production refers to the practice of getting ready for producing a few items to test real-life manufacturing processes. It helps to understand if there are any manufacturability concerns and that the production processes are viable and reproducible.
Troubleshooting and Debugging
In pilot production you mainly solve all the manufacturability related issues. You need to perform documentation and testing activities comprehensively during this stage to eradicate every possible challenge before it gets to the production phase.
Process Refinement
The production processes should follow adjustment and improvements in accordance with the feedback of the pilot production. This makes it possible to produce large quantities of products as desired because you can repeat the steps in a similar manner. Process refinement plays a crucial role in manufacturing to ensure that it produces high-quality products and provides efficient production.
6. Mass Production
Scaling Up Production
While moving from pilot production to mass production, the organization needs to expand its production capability to match that of the market. This is because it has to be well planned and co-ordinated so that the production processes deal with the increased volume.
Quality Control
The practice of proper quality assurance is critical when producing a large number of items. This entails periodic examination and appraisal for adequacy in production of high quality products. It is paramount to make sure that services and goods quality up to the mark to ratin customers loyalness.
Management of Supply Chain
Any manufacturing venture that involves mass production must ensure that management of supply chain is effective. This includes handling of suppliers, transport and stock in order to ensure that there is effective and efficient acquisition of resources at the right time and cost. Management of supply chain can play a major role in reducing delays and hence the cost of production.
7. Product Launch
Marketing and Sales Strategy
The marketing and sales strategies are important in the overall formulation of the company’s marketing and sales plan of the new product. This entails carrying out a market research, defining the consumers and developing a marketing plan. Market oriented product launches are essential in that they assist in achieving maximum results and sales.
Distribution and Logistics
Logistical planning for product distribution also makes it easy to deliver the product to the targeted customers. This encompasses working with distribution channel associates, stocking and delivering products as appropriate. A good distribution and logistics channel is very important when it comes to satisfying the customers.
Post-Launch Support
Ensuring customers support and feedback collection is crucial after the launch of a new product. It assists in realizing some weaknesses and strengths which you need to work on. Strategic process improvement based on customer feedback guarantees sustainability and customer satisfaction.
Summary
The NPI new product introduction process is a system that followed many stages, these stages are the conceptual and design stage, optimization stage, prototyping stage, pre- production stage, production stage and marketing stage. All of them are vital for addressing issues like product quality, cost, and the time to market.
A good NPI process can greatly affect these aspects of a product, its competitiveness, as well as the reputation of the company behind the product. It confirms that it will meet the needs of consumers, be inexpensive to produce, and adequately prepared for assembly-line production and release to the marketplace.
Some of the emerging trends and technologies seen on the NPI process include; prototyping technologies, automation, and digital manufacturing. These trends if followed provide additional improvements to the NPI process in terms of efficiency and effectiveness, as well as equip businesses for the next tests in product introduction.


