The Ultimate Guide to Sheet Metal Blanking: Applications, Methods and Advantages

Many processes help industries achieve the best out of raw metals. Procedures like sheet metal blanking play an integral role in metal fabrication. This process maintains accuracy and precision, helping manufacturers achieve high-quality results and ensure desired production.
Table of Contents
ToggleFrom the automotive and aerospace industry to consumer products, it has gained significant attention for its optimal performance. Moreover, it offers high repeatability, fidelity, and reliability in part formation. It delivers high quality, smooth finish that requires minimal post-processing. Furthermore, it brings economical pros when employed for large-volume production.
This article will discuss the importance of sheet metal blanking, highlighting its process, applications, and advantages across various sectors worldwide.
Sheet Metal Blanking: An Overview
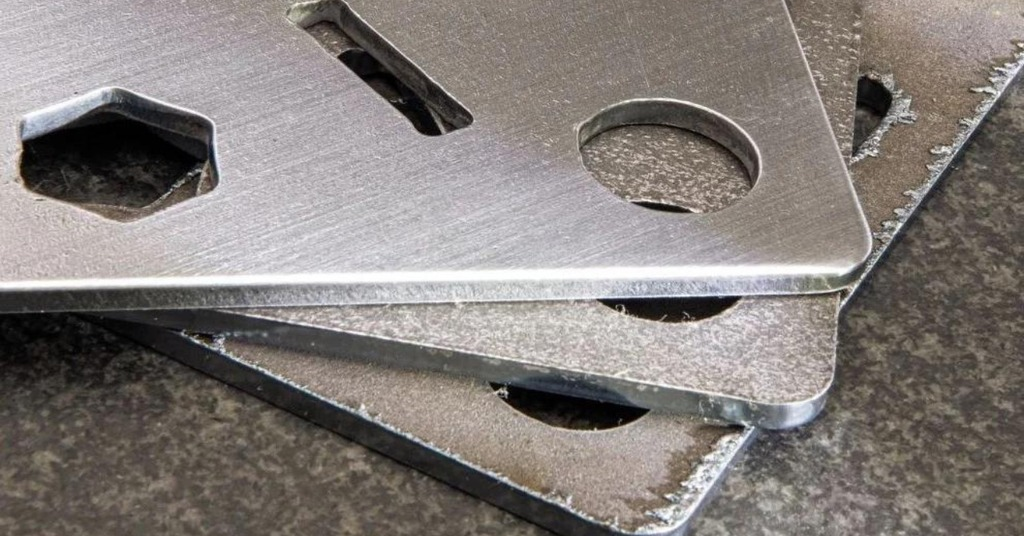
Sheet metal blanking refers to a sheet metal separation process in which fabricators use a punch-and-die system for the extraction of a specific part from a large flat metal sheet.
Sheet Metal Blanking
In some sectors, it is recognized by the name of shearing. Shearing is the process of removing small parts by force that come out from a punch. After punching and cutting, the process helps fabricators extract a piece referred to as “blank.” Machine operation can produce multiple blanks from various sheets simultaneously. This method contributes to the process of sheet metal fabrication which also assembles the metallic products.
Sheet metal blanking: Youtube
Sheet Metal Stamping Vs. Sheet Metal Blanking: Key Differences
However, both stamping vs. blanking are used interchangeably, but with distinct approaches. These are types of metal fabrication techniques. Blanking involves punching metal sheets into desired blanks. Stamping, on the other hand, follows the same workflow as blanking. But, in its case, the die contains the desired configuration, and the job material (Metal Sheet) is placed on the die. Similarly, punch applies force to shear the workpiece to the desired outcome.
They help in the production of machines and finished parts for various sectors; including automotive, aerospace, medical, and consumer products.
What are The Types of Sheet Metal Blanking?
Sheet metal blanking involves different sets of methods. Each type offers unique advantages while also having its limitations.
However, several factors can influence the sheet metal blanking process including, the hardness of material, thickness, and its type. The punch design also plays an important role here.
Listing down all these critical factors before starting the metal sheet blanking process is necessary. This helps in optimizing the operation while tracking each cycle for the best results.
Here are some most common types of sheet metal blanking.
Mechanical Blanking:
Fabricators employ motors to exert a high force on sheet metal in mechanical blanking. These motors transform the rotational force into vertical force, thus executing the shearing operation swiftly. This is why the use of mechanical press is a popular choice across various industries as it ensures speedy iteration and precision for large production volumes in minimal turnaround.
Mechanical press machines generally include a shank, metal strip, die block & holder, punch plate, and a bed or press. All these components ensure accurate execution of the press.
Hydraulic Blanking:
Hydraulic Press For Sheet Metal Blanking
In this type of sheet metal blanking, operators use hydraulic pressure machines to force the punch into the metal sheets. Hydraulic metal sheet blanking offers more control over the process as it uses a reliable fluid and valve system.
This process employs a hydraulic pressure stemming that passes a fluid through a pump. Operators can execute extended blanking operations and produce delicate results. That’s why this hydraulic blanking is recommended for blanking sophisticated geometries. However, it is relatively slower and can be costly for large production volumes.
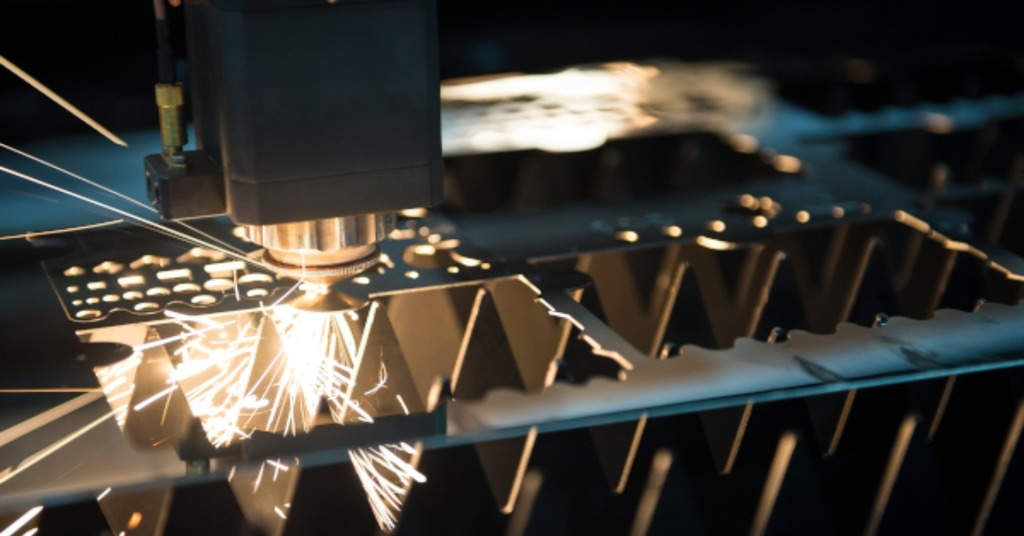
Laser Blanking:
Laser Blanking
Laser blanking uses a high-power laser to cut through sheets. This highly intensive laser can pierce through large sheets of metal resulting in precise blanks. It is an ideal choice when it comes to cutting complex shapes from materials that have high resistance to impact. Laser cutting enables operators to cut through even the hardest metals that present a significant challenge through general blanking methods.
Sheet Metal Blanking Process: A Deep Dive
There are several steps involved in sheet metal blanking. The operation is majorly around three components; for instance;
- Press
- Punch
- Die
Firstly, the operator placed the selected sheet of metal onto the die. Then a high-impact force is applied to make a blanks or contours into a metal sheet. The sheet material blanking process allows engineers to craft extracted shapes from a large number of sheets swiftly. These three essential components enable effective blanking using different machines. Each type of metal sheet blanking such as mechanical, hydraulic, and laser utilizes these parts.
The press, punch and die all three contribute to the process of shearing. Let’s understand how these components work in detail.
Steps involved in Sheet Metal Blanking
There are numerous steps manufacturers should count on during sheet metal blanking. However, in general, these five core steps are well-known across industries.
- Selecting the Right Material: The first and foremost step is to select the sound material for the intended application. Selecting appropriate material is necessary as it ensures the suitability of the process. The ultimate choice depends upon key factors such as; strength-to-weight ratios, durability, workability, and corrosion resistance. Mostly, manufacturers employ aluminum, carbon, steel, and brass. Among these, aluminum offers high durability and workability. Aluminum metal is highly recyclable too which makes it a go-to choice for fabricators for household to industrial equipment production.
- Punch and Die Designing:
Punch and Die
- Then comes the punching and die designing phase. Fabricators make sure to match both these parts as per the requirements, i.e., the desired geometry of the finished part. In this step, they create a detailed drawing that covers all the key details of the punch and die. These measurements include the dimensions, tolerances, and pressure constraints for creating the desired shape after the blanking process. The punch performs blanking while die blocks ensure the clamping of the workpiece accurately.
- Blanking Equipment Setup: It’s crucial to align the punch and die correctly for the desired blank. In this step, the fabricator aligns the material first, along with punch and die. All the pressure adjustments are also part of this process, such as setting the appropriate force for the specific sheet metal blanking.
- The Blanking Operation: After the equipment is all set, fabricators operate the blanking machine. In this process, they force the punch through the sheet metal using a suitable machine. This results in a clear cut within the metal in the desired shape. The sheet metal blanking process depends on the material properties as mentioned already in step one. Thus, depending on the type of metal, it may become necessary to repeat the blanking process multiple times to complete the cut. This is mainly for hard and thick metal sheets and is not implemented for common light-weight metals.
- Inspection and Finalization: Lastly, it is necessary to finalize the cut using standard industrial practices. This step involves the quality inspection of the blank that may require deburring to remove any rough surface edges. In this way, surface finishing helps eradicate all the imperfections. Mostly, fabricators implement deburring processes such as barrel tumbling, thermal deburring, and vibratory finishing, manual deburring. All these methods depend on the type of metal and the need for tweaking. The end product is then further put under additional analysis to ensure that it fulfills all the requirements of dimensions and tolerances.
Sheet Metal Blanking Techniques
There are various methods exploited for sheet metal blanking. Some of the most commonly used methods are mentioned below:
- Fine Blanking: Fine blanking or fine-edge blanking method compresses the whole material sheet before blanking. It uses two punches, the top and another at the bottom for the compression of the sheet. The fine blanking method helps companies achieve tighter tolerances and minimizes the possibility of burr after cutting. This method produces smoother edges while reducing polishing costs.
- Continuous Strip Blanking: As the name suggests, this technique uses the continuous addition of metal sheets into the press. This feeding of metal sheets for blanking is called continuous strip blanking and helps in the accurate reproduction of a large number of sheets. This method is pivotal in large-scale industrial productions of parts such as bottle caps, medals, and coins.
- Compound Die Stamping: Another key method of sheet metal blanking is compound sheet die stamping. This technique helps in the production of most complex parts, especially using steel. In this method, engineers feed the metal to the fast-output compound stamping machine. It accurately stamps the metal for the production of steel parts at a large scale.
- Progressive Die Stamping: This method is different from compound stamping as it uses sheet metals in coiled strips. The machine stamps, trims, and bends the coils of metal. This results in the formation of conjoined strips that separate into identical and individual components.
Metals Used In Sheet Metal Blanking
Sheet metal blanking uses various metal types; for instance, aluminum, steel, brass, and iron. Each metal possesses distinct features such as flexibility, formability, and manufacturability. Let’s discuss the compatibility of these metals in detail;
Steel:
Various grades of steel are used for the sheet metal blanking process. Chromium in steel imparts great resistance to corrosion making it well suited to the blanking process. Moreover, it offers various grades such as;
- Stainless steel
- Carbon steel
- Iron steel
- Galvanized
The high corrosion resistance ability of steel against chemicals, acids, and bases makes it a sound option for marine, automotive, aerospace, and medical device applications.
Aluminum:
Aluminum possesses great formability and ductility to ease manufacturability. It’s economical to use aluminum for blanking purposes as it usually comes at a low cost when compared to other metals. Moreover, it’s a versatile metal that finds extensive use in structural automotive, and aerospace industries.
Iron:
Iron is among the tenacious metals. This fascinating feature of iron makes it suitable for blanking sheet metal for shaping constructional frameworks.
Copper:
Copper is an irreplaceable metal where conductivity is paramount. The high conductivity of copper makes it sound for cutting metal techniques, for instance; laser cutting, plasma cutting, and waterjet cutting.
Alongside, it is also used for metal fabrication for making valve guides, gears, radiators, and fasteners.
Deburring Methods in Sheet Metal Blanking
Deburring in sheet metal
The operation of eliminating irregular surfaces such as sharp edges and burrs from the workpiece is called deburring. It is common practice after sheet metal blanking and machining to refine the product and give it a smooth surface for a longer lifespan. Different deburring methods used in the industry are:
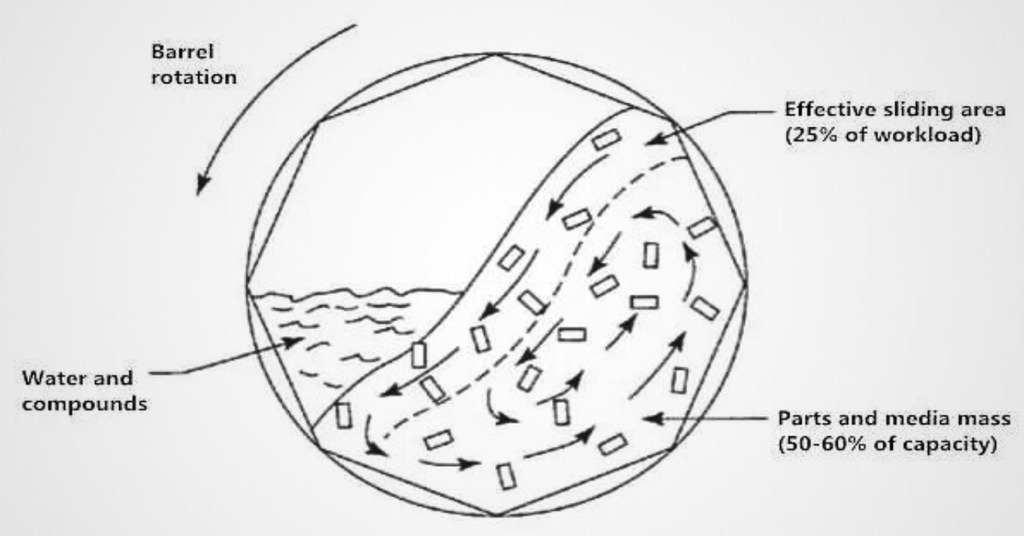
Barrel Tumbling
One of the most common finishing methods is barrel tumbling. In this deburring process, the workpiece is placed in a barrel that contains cleaning compounds. The barrel is generally 6 or 8-sided and keeps on rotating at a specific speed. This creates a centrifugal force that cleans the surface.
Electromechanical Deburring
Also referred to as ECMB, this deburring process removes irregular edges using anodic metal dissolution. The tool acts under a DC in the presence of an electrolyte that causes a reaction with the workpiece, removing the burrs in a precise manner.
Manual Deburring
Manual Deburring
Manual deburring is the technique of refining the workpiece using simple hand tools. This process is relatively easier. However, it is time-consuming and lacks efficiency.
Thermal Deburring
The thermal deburring method uses heat to produce pressure and remove the inaccessible burns. In this process, a spark ignition system is used to heat the compressed gases within the pressurized chamber. This causes the temperature to go up to 6000°F for a few milliseconds, removing the burrs.
Vibratory Finishing
Vibratory finish
In the vibratory finishing process, the workpiece is placed into a vibratory tumbler. Within the tumbler, specialized pellets are added along with other compounds. The vibratory bowl creates a consistent motion to create friction. This smoothens the surface of the workpiece.
Industrial Applications of Sheet Metal Blanking
Sheet metal blanking has a lot of real-world applications. Here are some common industrial use cases of sheet metal blanking.
Automotive:
The automotive sector is a primary consumer of most custom metallic products. It implements the sheet metal blanking process to customize the metals as per their requirements. As different automotive companies have unique sets of components for their vehicles, the manufacturers use sheet metal blanking to create unique types of products. These include body panels, structural parts, interior blueprints, and brackets.
Aerospace:
The sheet metal blanking plays a pivotal role in the aerospace sector. This technique is highly economical when it comes to large-scale production of aviation components. Metal durability, toughness, and long-term reliability are key concerns for these sectors. They exploit sheet metal blanking to cut through lightweight yet high-strength components. Some examples include; airframe, landing gears, and jet engine components. These parts are integral for aircraft and spacecraft functionality and long-term work.
Construction:
Construction and infrastructure development is one of the primary sectors that consumes metals on a large scale. Modern-day building requires different types and shapes of metallic structures that are feasible for modern building designs. Other components that implement sheet metal blanking for manufacturing include roofing elements, siding, and structural parts.
Electronics:
Metals also have a significant role in the electronics sector. They offer versatile usability to this industry as electronics manufacturers can use different conductivities of metals for their good. They mostly manufacture circuit boards that many housing projects implement. Other than that, heat sinks and holders use sheet metal blanking to cut the required metal into specified shapes.
Appliances:
Daily appliances come in different sizes and shapes. The sheet metal technique is well suited to these applications. These products use a sheet metal blanking process to meet the demands of modern appliances. Some common examples are washing machines, refrigerators, and ovens. Metallic properties such as conductivity play a crucial role in this regard.
Technologies for Sheet Metal Blanking
Sheet metal bending is highly influenced by innovative technologies. Industries use different techniques to increase the efficiency of the process. Here are some key innovations that further enhance the sheet metal blanking process:
- Fiber-laser cutting: Fiber-laser cutting is the latest technology that enhances the working rate of blanking machines. This technology significantly increases the cutting speeds that no traditional blanking methods can achieve.
- Automation: Automation has revolutionized this technique. CNC systems improve efficiency and result in highly perfect blanking with minimal to no human error.
- Servo Motors: These motors are advancements in the field of mechanical sheet metal blanking. These motors control the punch and die, enabling more control over the process with higher precision.
Benefits of Sheet Metal Blanking
Sheet metal blanking offers great advantages to manufacturers. Some of them are listed below:
- Maximum Use of Material: Manufacturers can consume the maximum amount of material as blanking generates minimal waste. This is a big upside as it reduces costs and makes the process environmentally friendly.
- Higher Efficiency: As discussed above, newer technologies increase the efficiency of the sheet metal blanking process, making it relatively fast and feasible for high-volume production of goods.
- Complete Accuracy: The sheet metal blanking process provides complete accuracy if the initial setup is correct. It allows fabricators to achieve tight tolerance for intricate feature designs with high precision, and accuracy.
- Versatility: Sheet metal blanking facilitates a versatile process, meaning it can produce a wide range of products for multiple sectors. Due to the wide range of material options, manufacturers can benefit from employing metal blanking for various applications.
- Minimal Need for Post Processing: For most metals, the blanking process produces products that need minimal smoothening or finishing. It results in a clean surface that is ready for further use.
How Maison Brings Precision In Your Metal Fabrication Projects?
At Maison, our engineers and expert fabricators ensure preeminence in your sheet metal fabrication projects. Here, we use the latest robotic welding, shearing, and drilling techniques. Our In-demand machining services help you achieve tighter tolerances with high precision and in a short turnaround.
Our comprehensive services cover a wide range of material options intended for your specified project requirement. The punching machines, welding, and CNC technologies ensure the bending and forming of materials with the highest accuracy. Moreover, we cover all the key areas of production, from metal bending, cutting, and shrinking to stretching.
Contact us today to get a complete walk through for your specific project. Drop your queries for an instant free quote!
Conclusion
Sheet metal blanking has become a fascinating fabrication process. It ensures the production of sophisticated parts with exceptional accuracy.
Manufacturing Industries implement different types of blanking depending on their production requirements. Moreover, it offers compatibility with a wide range of metals, including, steel, aluminum, iron, etc. It has several advantages for manufacturers including low waste, high precision, and precise configuration in a short turnaround.
However, there are different factors to take care of before starting the blanking process such as the design of the punch and die. Pressure or force constraints are also necessary to address for each metal type as they directly impact the end product quality. Ultimately, sheet metal blanking can provide top-quality production of parts and components to meet all the process requirements.
FAQs:
Q1. What is the tolerance for metal sheet blanking?
The tolerances depend upon material properties such as strength and thickness. The layout of the part also determines the overall tolerance. In general, tolerances between ±0.0003–0.002 inches are possible to achieve.
Q2. What is the speed of fine metal sheet blanking?
Normally, fine sheet metal blanking has an operating speed range between 3 to 15 mm/min.
Q3. What metals are compatible with sheet metal blanking?
Various metals are widely adopted for sheet metal blanking. For instance, aluminum, steel, copper, and iron, etc. Other than sheet metal, the punch and die are integral to the process.
Q4. Is blanking is same as piercing?
Although both processes are used for metalworking, there are differences between them. Piercing is used for creating holes in the sheet metal while blanking is a cutting process useful to cut out flat shapes (Blanks). The primary function of piercing is to create openings for fasteners.
Resources:
Investigation of Sheet Metal Blanking Process, Retrieved From Springer Link
Blanking: Science Direct

Send Your Inquiry Today
+86-18969433502
sales@sheetmetalmasion.com